Known to many since childhood. Someone himself was seriously fond of the myths of ancient Greece, someone instilled a love of ancient culture in school. It would seem strange to transfer this knowledge into adulthood, because all this is actually a myth.
Short introduction:
However, the ancient Greek gods and the events that happen to them are reflected in many works of literature and cinema, almost all modern plots are taken from antiquity.
Knowledge of the gods of ancient Greece- a prerequisite for understanding a variety of philosophical issues. That is why every person is simply obliged to know as much as possible about the famous gods from Olympus.

Generations of the gods of ancient Gretsii
- Distinguish several generations ancient Greek gods.
- At first there was only haze from which Chaos was formed. Joining together, haze and chaos gave birth to Erob, who personified darkness, Nyukta, or as it is also callednight, Uranus - heaven, Eros - love, Gaia - mother earth and Tartarus, which is an abyss.

I generation of gods
- All the heavenly gods appeared thanks to the union of Gaia and Uranus, the sea deities originated from Pontos, the union with Tartas led to the emergence of giants, while earthly beings are the flesh of Gaia herself.
- In principle, all the ancient Greek gods descended from her, it was she who invented the names, giving life.
- Usually the goddess of the earth was depicted as a rather large woman who rises half above the planet ..
- Uranus was the ruler of the universe. If he was depicted, it was only in the form of an all-encompassing dome of bronze, covering the whole world.
- Together with Gaia they gave birth to several titan gods:
- The ocean (all the world's waters, represented a horned bull with a fish tail),
- Tefida (also titanide), Thea, Rhea, Themis, Mnemosyne like a goddess of memory
- Krius (this titan had the ability to freeze), Kronos.
- In addition to the titans, the Cyclops are considered the children of Uranus and Gaia. Hated by their father, they were sent down to Tartarus for a long time.
- For a long time, the power of Uranus defied comparison, he solely ruled over his children, until one of them, Kronos, otherwise called Chronos, decided to overthrow his father from the pedestal.
- The time lord managed to remove his father Uranus by killing him with a sickle. As a result of the death of Uranus, the great titans and titanids appeared on earth, who became the first inhabitants of the planet. Gaia also played a certain role in this, she could not forgive her husband for the expulsion of the firstborn of the Cyclops to Tartarus. From the blood of Uranus emerged Erinias, creatures who patronized blood feud. Kronos thus achieved unprecedented power, but the expulsion of his father did not pass unnoticed by his own personality.
- Kronos's wife was his own sister, the Titanide Rhea. When Kronos became a father, he was madly afraid that one of his children would also turn out to be a traitor. For this, attitan devoured the rank of his offspring, as soon as they had time to be born. The fears of Kronos were justified by one of his sons, the great Zeus, who sent his father into the darkness of Tartarus.
II generation of gods
- Titans and Titanides are the second generation of ancient Greek gods.
III generation of gods
- The most famous and familiar to modern man is third generation.
- As already clear, Zeus became the main one among them, he was the unconditional leader, all living things on earth were strictly subordinate to him.
- Besides Zeus t third generation of gods Ancient Greece has 11 more Olympian gods.
- Their wide popularity is based on the fact that thesethe gods, as legends say, descended to people, participated in their lives, while the titans always remained aloof, lived their own lives, each fulfilling their functions separately.
- All 12 gods lived , based on myths, on Mount Olympus. Each of the gods performed their own specific function, had their own talents. Each had a unique character, which was often the cause of human sorrow, or, conversely, joy.
And now about the most famous gods in more detail in a short performance ...
Zeus

Poseidon

The rest of the gods
- Each of the gods described was incredibly powerful and very revered in ancient Greece, but the third, most famous generation consisted not only of them.
- The descendants of Zeus also adjoined him. Among them, the common children of the Thunderer and Hera can be distinguished.
- For example, Ares personified masculinity, he was often called the god of war. Ares never and nowhere appeared alone, was always accompanied by two faithful companions: Eris, the goddess of strife and Enio, the goddess of war.
- His brother Hephaestus was worshiped by all the masters of blacksmithing, he was also a fire-maker.
- He was unloved by his father, because outwardly he was very ugly, and limped.
- Despite this, he had a total of two wives, Aglaya, and the beautiful Aphrodite.
Aphrodite

Hera was the last, but not the only wife of Zeus. His second wife Themis was absorbed by the Thunderer even before Athena was born, but this did not prevent the birth of one of the great goddesses.
Athena was born by her father, Zeus himself, and came out of his head. Represents war, but not only. She is also known as the embodiment of wisdom and crafts. All the ancient Greeks turned to her, but especially the inhabitants of the city of Athena, since the young goddess was considered the patroness of this settlement.
Less known in wide circles is the other daughter of Zeus and Themis, Ora, who personified the seasons. In addition, the daughter of Zeus and Themis is also credited with the three goddesses Kloto, Lachesis and Atropos, who were collectively called simply Moira.
The first, Clotho spun the threads of life, Lachesis determined human destiny, and Anthropos personified death. However, not all sources of information call Moira the daughters of Zeus; there is another version, according to which they were daughters of the night.
One way or another, all three sisters were constantly in close proximity to the supreme god, helping him keep track of people, and predetermining many different destinies.
On this, the children of Zeus, born in legal marriage, end, and a whole galaxy of illegitimate, but from this no less revered and respected, descendants begins. These are the twin brother and sister Apollo, who was the patron saint of music, and the predictor of the future, and Artemis, the goddess of the hunt.
They appeared with Zeus after a relationship with Leto. Artemis was born earlier. Talking about her, not only the image of a huntress, but also a pure and immaculate virgin pops up in my head, since Artemis embodied chastity, was not loving, more precisely, there is not a single confirmation of her possible romances.
But Apollo, on the contrary, is known not only as a golden-haired youth and the embodiment of light, but also for his numerous love affairs. One of the love stories became very symbolic for the young god, leaving an eternal reminder of itself in the form of a laurel wreath that crowned the head of Apollo.
Another illegitimate son, Hermes, was born of the Pleiades of Maya. He patronized traders, orators, gymnasiums and sciences, and was also the god of animal husbandry. During his lifetime, the ancient Greeks asked Hermes for the gift of eloquence, and after death they relied on him as a faithful guide on their last journey. It was Hermes who accompanied the souls of the dead to the kingdom of Hades. It is widely known, among other things, thanks to its permanent attributes: winged sandals and an invisibility helmet and a staff decorated with a metal weave in the form of snakes.
In addition, it is also known about the illegitimate daughter of Zeus, Persephone, born of the goddess Demeter, as well as about the son of Dionysus, who was born into the world by a simple mortal woman Semele. Dionysus was nevertheless a full-fledged god, the patron saint of the theater.
Ariadne became his wife, which brought Dionysus closer to greatness even more, making him also one of the most famous gods of ancient Greece. Other children of Zeus are known, born of mortal women. This, for example, Perseus, who was born into the world by the Argos princess Danae, the famous Helen is also the daughter of Zeus, the Spartan queen Leda became her mother, the Phoenician princess gave the thunderer another descendant of Minos.
All the Olympic gods led a calm measured lifestyle, succumbing to hobbies, mortal passions, fleeting amusements, while not forgetting to fulfill each of their direct duties. Life on Olympus was not so easy, due to the numerous feuds and intrigues between various gods. Each tried to prove his power, while not encroaching on the responsibilities of the other, therefore, sooner or later a compromise was reached. But not all the gods of ancient Greece were lucky enough to live on Mount Olympus, some of them lived in other, less well-known places. These are all those who, for whatever reason, fell out of favor with Zeus, or simply did not deserve his recognition.
In addition to the Olympian gods, there were others. For example, Hymen, who was the patron saint of marriage. He was born thanks to the union of Apollo and the muse Calliope. The goddess of victory Nika was the daughter of the titan Pallat, Iris, who personified the rainbow, was born by one of the Oceanids, Electra. Ata can also be distinguished as the goddess of gloomy reason, her father was the famous Zeus. The child of Aphrodite and Ares Phobos, the god of fear, lived separately from his parents, just like his brother Deimos, the lord of horror.
In addition to the gods in ancient Greek mythology, muses, nymphs, satyrs and monsters are also distinguished. Each character is thought out and individual, carries some idea. Each has a certain type of behavior, thinking, perhaps it is thanks to this that the world of myths is so many-sided, and arouses particular interest in childhood.
In conclusion, I must say ...
The above gods are just a short version. Naturally, this list of gods cannot be called complete. In order to tell about all, without exception, the gods of ancient Greece, hundreds of books are not enough, but everyone is obliged to know about the existence of the above. If for the inhabitants of ancient Greece the pantheon of gods served as an excuse for all kinds of objects and phenomena, then for modern man the images themselves are curious.
Not their material environment and not the grounds that prompted the birth of such heroes, namely the allegories that they evoke. Otherwise, it will be impossible to understand all the ancient Greek myths and legends. Almost any text written in antiquity has references to one or more of the main gods of both the first and second and third generations.
And since all literature and theater of our time are in any case built on ancient ideals, every self-respecting person is obliged to know these ideals. The images of Zeus, Hera, Athena, Apollo have long become household names, today they are very archetypal, and, oddly enough, are understandable to everyone.
Simply because it is not necessary to get seriously involved in Greek mythology in order to know the famous story of the Apple of Discord. And there are many such examples. Therefore, the gods of ancient Greece are not just passing characters from childhood, they are what absolutely every educated adult should know.
Hades- God is the lord of the kingdom of the dead. Antaeus- the hero of myths, a giant, the son of Poseidon and the Land of Gaia. The earth gave its son strength, thanks to which no one could cope with him. Apollo- the god of sunlight. The Greeks portrayed him as a handsome youth. Ares- the god of treacherous war, the son of Zeus and Hera. Asclepius- the god of medical art, son of Apollo and the nymph Koronis Borey- the god of the north wind, the son of the Titanids Astrea (starry sky) and Eos (dawn), brother of Zephyr and Nota. He was depicted as a winged, long-haired, bearded, mighty deity. Bacchus- one of the names of Dionysus. Helios (Helium)- the sun god, brother of Selena (goddess of the moon) and Eos (dawn). In late antiquity, he was identified with Apollo, the god of sunlight. Hermes- the son of Zeus and Maya, one of the most ambiguous Greek gods. Patron saint of wanderers, crafts, trade, thieves. Possessing the gift of eloquence. Hephaestus- the son of Zeus and Hera, the god of fire and blacksmithing. He was considered the patron saint of artisans. Hypnosis- the deity of sleep, the son of Nikta (Night). He was portrayed as a winged youth. Dionysus (Bacchus)- the god of viticulture and winemaking, the object of a number of cults and mysteries. He was depicted in the form of an obese elderly man, then in the form of a young man with a wreath of grape leaves on his head. Zagrei- the god of fertility, the son of Zeus and Persephone. Zeus- the supreme god, the king of gods and people. Marshmallow- the god of the west wind. Iacchus- the god of fertility. Kronos- the titan, the youngest son of Gaia and Uranus, the father of Zeus. He ruled the world of gods and people and was overthrown from the throne by Zeus .. Mom- the son of the Goddess of the Night, the god of slander. Morpheus- one of the sons of Hypnos, the god of dreams. Nereus- the son of Gaia and Pontus, a meek sea god. Music- the god of the south wind, depicted with a beard and wings. Ocean- the titan, the son of Gaia and Uranus, brother and husband of Tefis and the father of all the rivers of the world. Olympians- the supreme gods of the younger generation of Greek gods, led by Zeus, who lived on the top of Mount Olympus. Pan- the forest god, the son of Hermes and Driopa, a goat-legged man with horns. He was considered the patron saint of shepherds and small livestock. Pluto- the god of the underworld, often identified with Hades, but unlike him, who owned not the souls of the dead, but the riches of the underworld. Plutos- the son of Demeter, the god who gives people wealth. Pont- one of the older Greek deities, the offspring of Gaia, the god of the sea, the father of many titans and gods. Poseidon- one of the Olympian gods, brother of Zeus and Hades, who rules over the sea element. Poseidon was also subject to the bowels of the earth, he ruled storms and earthquakes. Proteus- sea deity, son of Poseidon, patron saint of seals. He possessed the gift of reincarnation and prophecy. Satyrs- goat-footed creatures, demons of fertility. Thanatos- the personification of death, the twin brother of Hypnos. Titans- the generation of Greek gods, the ancestors of the Olympians. Typhon- a hundred-headed dragon born of Gaia or a Hero. During the battle between the Olympians and the Titans, he was defeated by Zeus and imprisoned under the Etna volcano in Sicily. Triton- the son of Poseidon, one of the sea deities, a man with a fish tail instead of legs, holding a trident and a twisted shell - a horn. Chaos- an endless empty space, from which at the beginning of time emerged the most ancient gods of the Greek religion - Nikta and Erebus. Chthonic gods- deities of the underworld and fertility, relatives of the Olympians. These included Hades, Hecate, Hermes, Gaia, Demeter, Dionysus, and Persephone. Cyclops- giants with one eye in the middle of the forehead, children of Uranus and Gaia. Evr (Heb)- the god of the southeast wind. Aeolus- the lord of the winds. Erebus- the personification of the darkness of the underworld, the son of Chaos and the brother of the Night. Eros (Eros)- the god of love, the son of Aphrodite and Ares. In the most ancient myths - a spontaneous force that contributed to the ordering of the world. He was depicted as a winged youth (in the Hellenistic era - a boy) with arrows, accompanying his mother. Ether- deity of the sky
Goddesses of ancient Greece
Artemis- the goddess of hunting and nature. Atropos- one of the three moirs, cutting the thread of fate and ending human life. Athena (Pallas, Parthenos)- the daughter of Zeus, born from his head in full combat weapons. One of the most revered Greek goddesses, the goddess of just war and wisdom, the patroness of knowledge. Aphrodite (Kytherea, Urania)- the goddess of love and beauty. She was born from the marriage of Zeus and the goddess Dione (according to another legend, she came out of sea foam) Hebe- the daughter of Zeus and Hera, the goddess of youth. Sister of Ares and Ilithia. Served the Olympian gods at feasts. Hecate- the goddess of darkness, night visions and sorcery, the patroness of sorcerers. Hemera- the goddess of daylight, the personification of the day, born of Nikta and Erebus. She was often identified with Eos. Hera- the supreme Olympic goddess, sister and third wife of Zeus, daughter of Rhea and Kronos, sister of Hades, Hestia, Demeter and Poseidon. Hera was considered the patroness of marriage. Hestia- the goddess of the hearth and fire. Gaia- mother earth, foremother of all gods and people. Demeter- the goddess of fertility and agriculture. Dryads- lower deities, nymphs who lived in trees. Ilithia- the patron goddess of women in labor. Iris- the winged goddess, Hera's helper, messenger of the gods. Calliope- the muse of epic poetry and science. Kera- demonic creatures, children of the goddess Nikta, bringing people misfortune and death. Clio- one of the nine muses, muse of history. Clotho ("spinning")- one of the moira, spinning the thread of human life. Lachesis- one of the three moir sisters, determining the fate of each person even before birth. Summer- Titanide, mother of Apollo and Artemis. Mayan- a mountain nymph, the eldest of the seven pleiades - the daughters of Atlanta, the beloved of Zeus, from whom Hermes was born. Melpomene- the muse of tragedy. Metis- the goddess of wisdom, the first of the three wives of Zeus, who conceived Athena from him. Mnemosyne- the mother of nine muses, the goddess of memory. Moira- the goddess of fate, daughter of Zeus and Themis. Muses- the patron goddess of the arts and sciences. Naiads- nymphs-keepers of waters. Nemesis- the daughter of Nikta, the goddess, personifying, destiny and retribution, punishing people in accordance with their sins. Nereids- fifty daughters of Nereus and the oceanids Doris, sea deities. Nika- personification of victory. She was often depicted with a wreath, a common symbol of triumph in Greece. Nymphs- the lowest deities in the hierarchy of the Greek gods. They personified the forces of nature. Nikta- one of the first Greek deities, the goddess is the personification of the primordial Night. Orestiads- mountain nymphs. Ora- the goddess of the seasons, tranquility and order, the daughter of Zeus and Themis. Peyto- the goddess of persuasion, the companion of Aphrodite, often identified with her patroness. Persephone- the daughter of Demeter and Zeus, the goddess of fertility. The wife of Hades and the queen of the underworld, who knew the secrets of life and death. Polyhymnia- the muse of serious hymn poetry. Tefida- daughter of Gaia and Uranus, wife of Ocean and mother of Nereids and Oceanids. Rhea- the mother of the Olympian gods. Sirens- female demons, half-women, half-birds, capable of changing the weather at sea. Waist- the muse of comedy. Terpsichore- the muse of dance art. Tisiphon- one of the Erinyes. Tyche- the goddess of fate and chance among the Greeks, the companion of Persephone. She was portrayed as a winged woman standing on a wheel and holding a cornucopia and a ship's steering wheel. Urania- one of the nine muses, the patroness of astronomy. Themis- Titanide, goddess of justice and law, second wife of Zeus, mother of mountains and moir. Charites- the goddess of female beauty, the embodiment of a kind, joyful and eternally youthful beginning of life. Eumenides- another hypostasis of Erinyes, who were worshiped as goddesses of benevolence, who prevented misfortunes. Eris- daughter of Nikta, sister of Ares, goddess of discord. Erinia- the goddess of vengeance, the offspring of the underworld, punishing injustice and crime. Erato- Muse of lyric and erotic poetry. Eos- the goddess of the morning dawn, sister of Helios and Selena. The Greeks called her "pink-fingered". Euterpe- the muse of lyric chants. She was portrayed with a double flute in her hand.Ancient Greece before the arrival of the Greeks was inhabited by the Pelasgian peoples. They did not assimilate further with the Greeks, having gone into oblivion. Thanks to them, according to Herodotus, the ancient Hellenes had a religion with the gods of Ancient Greece in its modern sense.
Characteristic features of the religion of Ancient Greece.
With the emergence of the first statehood of Hellas, about 3000 BC, religion began to play an increasing role in the life of the ancient Greeks. The main gods were titans, who personified the elements of nature.
The supreme god of the titans, Kronos, killed his father in the struggle for power. He feared the same fate and therefore devoured his sons. One of them was saved by Rhea, the wife of Kronos. His name was Zeus. When Zeus grew up, he forced his father to return the swallowed sons from his womb and, joining forces with other gods, began to fight the titans.
Elder gods
In these numerous battles, according to the myths of Ancient Greece, the gods, led by Zeus, won. After the victory, they shared power and went to live on the sacred Mount Olympus.
- Zeus began to rule the sky, lightning and thunder. He became the head of the pantheon of the twelve elder gods. All other gods obeyed him and considered him the fairest. The ancient Greeks installed a statue of Zeus, it was located on the island of Poseidon and reached 15 meters.

Rice. 1. Statue of Zeus on Poseidon Island.
- Seas and oceans began to rule Poseidon ... He was married to the goddess Amphitrite, from whom a son, Triton, was born. In anger, this god was terrible: he could cause a flood, or waves break the seaport. Where Poseidon walked on the ground, spring water began to beat. This god was revered by all sea travelers and sailors.
- Hades did not want to rule the earthly world and went to Tartarus, where he began to rule the kingdom of the dead. On a chain at the entrance to the underworld sat his faithful three-headed dog Cerberus, who did not let the living into Tartarus. Hades stole his beloved niece Persephone from Zeus and forced her to marry him. The ancient Greeks sacrificed a black bull to Hades. Usually it was laid in front of crevices or the entrance to a cave, which personified the entrance to the kingdom of the dead.
- The main female goddess among the Greeks was considered Hera ... The last wife of Zeus was the patroness of marriage and punished cruelly for betrayal of married people. The ancient Greeks worshiped her and asked for the birth of strong and healthy children.
- He was the god of sunshine and the crown of male beauty. In addition to spiritual purity, this god was endowed with the abilities of a healer. Later, the ancient Greeks revered him as the patron saint of the arts, including music.

Rice. 2. Apollo.
The religion of ancient Greece did not carry the symbols of immortality, the gods, like people, had completely human features: they fell in love, suffered, were capable of mercy or betrayal. In the view of the ancient Greeks, the gods conquered the world from the natural elements, made this world a better place and became its patrons and protectors.
- God of all boundaries separating one from the other, and roads was Hermes ... He had a sharp mind, resourcefulness, because he was the patron saint of trade, knew several languages and stood out for his brilliant manners. In addition to merchants, this god was revered by shepherds and travelers.
- Hephaestus - the god of fire - patronized the blacksmith's craft, while he himself was considered an unsurpassed blacksmith. He was lame on both legs, because, according to legend, he was thrown down by Zeus, for helping Hera to get out of the shackles.
- Ares - the god of unjust wars. He was the son of Zeus and Hera. Zeus secretly hated him for his wild and unbridled disposition. Ares loved wild fun and could start a conflict for no reason. He was married to Aphrodite.
All the Olympic gods and goddesses led a recreational lifestyle, indulging in intrigue and passion. Each of the gods was powerful in its own way, so strife very often ended in compromise.
TOP-4 articleswho read along with this
Lesser gods
The older gods had children, this generation was more numerous than the previous one, some of them:
- Dionysus - the god of fertility and winemaking. He patronized grape farming and dancing. According to the legends of Ancient Greece, Hera hated Dionysus and drove him crazy. Wherever Dionysus appeared, he was accompanied by unrestrained drunkenness, gratuitous fun and even murder.
- Helios - Sun God. This god performed the same functions as Apollo, was a solar deity, and at the same time the eyes of Zeus: he knew what was going on and where in the mortal world of people. In Greece, many statues have been erected in honor of Helios, one of them is called the Colossus of Rhodes and belonged to the Seven Wonders of the World. The statue reached 33 meters and stood on the island of Rhodes in the Aegean Sea.

Rice. 3. Colossus of Rhodes.
- Iris carried out small and large orders of the gods. She carried messages and messages to people about the gods of Olympus. The ancient Greeks also revered her as the goddess of the rainbow.
- Themis - the goddess of justice, protector of the unjustly accused. Helped Zeus unleash the Trojan War. The Greeks portrayed this goddess with a blindfold, which meant her impartiality. The cornucopia in the hands of Themis meant a measure of retribution for those who appeared before her fair trial.
According to the religion of Ancient Greece, you can recreate a picture of the life of the ancient Greeks.
The following table provides a short list and description of the gods of Ancient Greece:
|
Name of god |
What did you manage (la) |
Characteristic |
|
Sky, lightning and thunder |
The first of the gods to put in people the concepts of honesty, conscience and shame. He possessed a punishing power. |
|
|
Poseidon |
Seas and oceans |
Depicted with an angry face. He did not tolerate objections, did not tolerate insults. |
|
Underworld of the dead |
Often depicted as generous and hospitable. |
|
|
Home |
Jealous and power-hungry Hera severely punishes for adultery. |
|
|
Artemis |
Loves animals, although he patronizes hunting. |
|
|
Patronizes the art of blacksmithing, made lightning for Zeus himself, because he himself was an unsurpassed master blacksmith. |
||
|
Vegetation |
Patronized theaters, winemaking and dancing. |
|
|
Justice |
She was the first soothsayer. Summoned to the council of the gods of Olympus. She was considered the most impartial and fair judge. |
The worship of the god Dionysus, which came from the north of the Balkans, developed separately from the rest of polytheism. Over time, this veneration became monotheistic (monotheism is one god). It is generally accepted by historians that the worship of Dionysus was the first harbinger of the formation of the Christian religion.
What have we learned?
The religion of Ancient Greece, which is studied in grade 5, unlike other religions, endowed the gods with human features, which brought them closer to people and allowed contemporaries to better know the life of the ancient Greeks. In addition, although the Greeks believed in an afterlife, this did not serve as a basis for them to worship the gods.
Test by topic
Assessment of the report
Average rating: 4.7. Total ratings received: 458.
Rhea, belted by Cronus, bore him bright children - the Virgin - Hestia, Demeter and the golden-haired Hera, the glorious power of Hades, who lives under the earth, And the Provider - Zeus, the father of both immortals and mortals, whose Thunders thrill the wide earth. Hesiod "Theogony"
Greek literature originated from mythology. Myth- This is the idea of an ancient man about the world around him. Myths were created at a very early stage in the development of society in various areas of Greece. Later, all these myths merged into a single system.
With the help of myths, the ancient Greeks tried to explain all natural phenomena, presenting them in the form of living beings. At first, experiencing a strong fear of the elements of nature, people portrayed the gods in a terrible animal form (Chimera, Medusa Gorgon, Sphinx, Lernaean hydra).
However, later the gods become anthropomorphic, that is, they have a human appearance and they have a variety of human qualities (jealousy, generosity, envy, generosity). The main difference between the gods and people was their immortality, but for all their greatness, the gods communicated with ordinary mortals and even entered into love relationships with them, in order to give birth to a whole tribe of heroes on earth.
There are 2 types of ancient Greek mythology:
- cosmogonic (cosmogony - the origin of the world) - ends with the birth of Crohn
- theogonic (theogony - the origin of gods and deities)
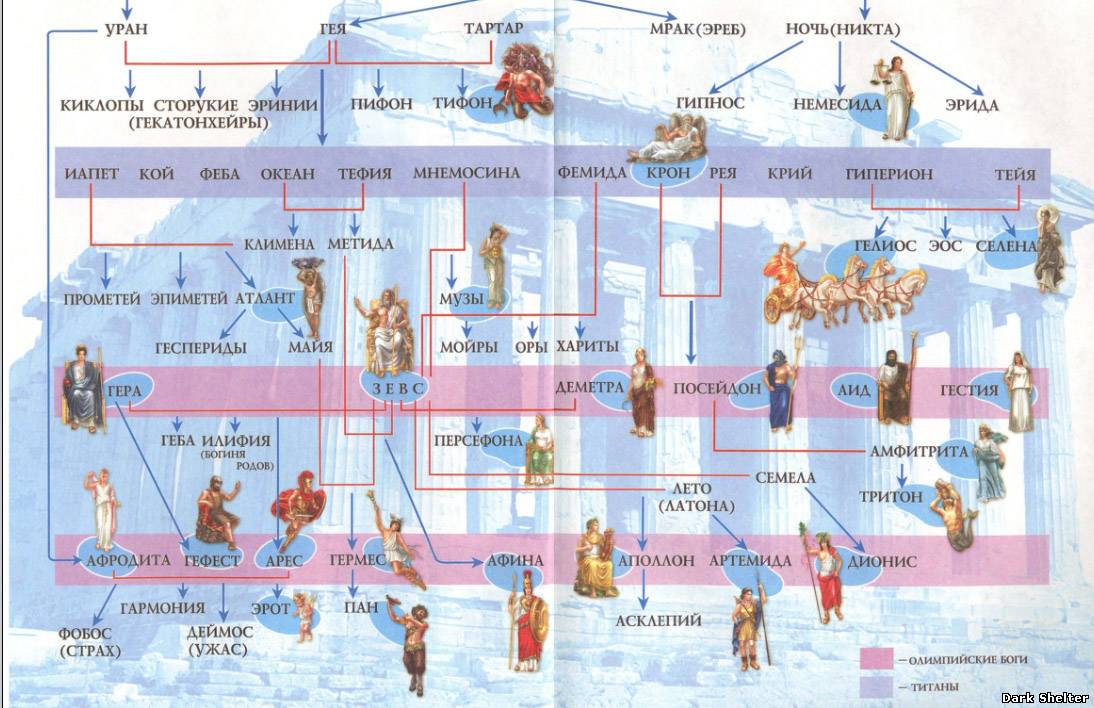
The mythology of Ancient Greece went through 3 main stages in its development:
- pre-olympic- it is basically a cosmogonic mythology. This stage begins with the idea of the ancient Greeks that everything came from Chaos, and ends with the murder of Cronus and the division of the world between the gods.
- Olympic(early classic) - Zeus becomes the supreme deity and with a retinue of 12 gods settles on Olympus.
- late heroism- from gods and mortals heroes are born who help the gods in establishing order and in destroying monsters.
On the basis of mythology, poems were created, tragedies were written, and lyricists dedicated their odes and hymns to the gods.

In ancient Greece, there were two main groups of gods:
- titans - gods of the second generation (six brothers - Ocean, Kei, Krius, Hiperion, Iapetus, Kronos and six sisters - Thetis, Phoebus, Mnemosyne, Theia, Themis, Rhea)
- olympic gods - the Olympians are the gods of the third generation. The Olympians included the children of Kronos and Rhea - Hestia, Demeter, Hera, Hades, Poseidon and Zeus, as well as their descendants - Hephaestus, Hermes, Persephone, Aphrodite, Dionysus, Athena, Apollo and Artemis. The supreme god was Zeus, who deprived the power of the father of Kronos (god of time).
The Greek pantheon of the Olympian gods traditionally included 12 gods, but the composition of the pantheon was not very stable and sometimes consisted of 14-15 gods. Usually these were: Zeus, Hera, Athena, Apollo, Artemis, Poseidon, Aphrodite, Demeter, Hestia, Ares, Hermes, Hephaestus, Dionysus, Hades. The Olympian gods lived on the sacred Mount Olympus ( Olympos) in Olympia, off the coast of the Aegean Sea.

Translated from the ancient Greek language, the word pantheon means "all gods". Greeks
Divided the deities into three groups:
- Pantheon (great olympic gods)
- Lower deities
- Monsters
Heroes occupied a special place in Greek mythology. The most famous of them:
v Odysseus
The supreme gods of Olympus
|
Greek gods |
Functions |
Roman gods |
|
god of thunder and lightning, sky and weather, law and fate, attributes - lightning (three-pronged pitchfork with notches), scepter, eagle or chariot drawn by eagles |
||
|
goddess of marriage and family, goddess of the sky and starry skies, attributes - diadem (crown), lotus, lion, cuckoo or hawk, peacock (two peacocks were carrying her cart) |
||
|
Aphrodite |
"Froth-born", the goddess of love and beauty, Athena, Artemis and Hestia were not subject to her, attributes - a rose, an apple, a shell, a mirror, a lily, a violet, a belt and a golden bowl, giving eternal youth, retinue - sparrows, doves, a dolphin, satellites - Eros, charites, nymphs, ora. |
|
|
god of the underworld of the dead, "generous" and "hospitable", attribute - a magic invisible hat and three-headed dog Cerberus |
||
|
the god of insidious war, military destruction and murder, he was accompanied by the goddess of discord Eris and the goddess of violent war Enio, attributes - dogs, a torch and a spear, there were 4 horses in the chariot - Noise, Horror, Shine and Flame |
||
|
god of fire and blacksmithing, ugly and lame in both legs, attribute - blacksmith's hammer |
||
|
goddess of wisdom, crafts and art, goddess of just war and military strategy, patroness of heroes, "owl-eyed", used male attributes (helmet, shield - aegis from the skin of an amalfea goat, decorated with the head of Medusa the Gorgon, spear, olive, owl and snake), was accompanied by Nika |
||
|
god of invention, theft, trickery, trade and eloquence, patron saint of heralds, ambassadors, shepherds and travelers, invented measures, numbers, taught people, attributes - a winged rod and winged sandals |
Mercury |
|
|
Poseidon |
god of the seas and all bodies of water, floods, droughts and earthquakes, patron saint of sailors, attribute - a trident that causes storms, breaks rocks, knocks out springs, sacred animals - bull, dolphin, horse, sacred tree - pine |
|
|
Artemis |
goddess of hunting, fertility and female chastity, later - the goddess of the moon, patroness of forests and wild animals, forever young, she is accompanied by nymphs, attributes - hunting bow and arrows, sacred animals - deer and bear |
|
|
Apollo (Phoebus), Kifared |
"Golden-haired", "silver-eyed", god of light, harmony and beauty, patron of arts and sciences, leader of muses, predictor of the future, attributes - silver bow and golden arrows, golden cithara or lyre, symbols - olive, iron, laurel, palm, dolphin , swan, wolf |
|
|
goddess of the hearth and sacrificial fire, virgin goddess. accompanied by 6 priestesses - vestals who served the goddess for 30 years |
||
|
"Mother Earth", the goddess of fertility and agriculture, plowing and harvest, attributes - a sheaf of wheat and a torch |
||
|
god of fruitful forces, vegetation, viticulture, winemaking, inspiration and fun |
Bacchus, Bacchus |
Secondary Greek Gods
|
Greek gods |
Functions |
Roman gods |
|
Asclepius |
"Revealing", the god of healing and medicine, an attribute - a staff entwined with snakes |
|
|
Eros, Cupid |
the god of love, the "winged boy", was considered the product of a dark night and a bright day, Heaven and Earth, attributes - a flower and a lyre, later - arrows of love and a flaming torch |
|
|
"The sparkling eye of the night", the goddess of the moon, queen of the starry sky, has wings and a golden crown |
||
|
Persephone |
goddess of the realm of the dead and fertility |
Proserpine |
|
the goddess of victory, depicted winged or in a pose of rapid movement, attributes - a bandage, a wreath, later - a palm tree, then - weapons and a trophy |
Victoria |
|
|
goddess of eternal youth, portrayed as a chaste girl pouring nectar |
||
|
"Rosy-fingered", "beautiful-curled", "golden-blooded" goddess of the morning dawn |
||
|
goddess of happiness, chance and luck |
||
|
the sun god, owner of seven herds of cows and seven flocks of sheep |
||
|
Cron (Chronos) |
god of time, attribute - sickle |
|
|
goddess of violent war |
||
|
Hypnos (Morpheus) |
||
|
goddess of flowers and gardens |
||
|
god of the west wind, messenger of the gods |
||
|
Dike (Themis) |
the goddess of justice, justice, attributes - scales in the right hand, a blindfold, a cornucopia in the left hand; the Romans put a sword in the goddess's hand instead of a horn |
|
|
god of marriage, conjugal bonds |
Thalassius |
|
|
Nemesis |
the winged goddess of revenge and retribution, punishing violation of social and moral norms, attributes - scales and bridle, sword or whip, chariot drawn by griffins |
Adrastea |
|
"Golden-winged", goddess of the rainbow |
||
|
goddess of the earth |
In addition to Olympus in Greece, there was a sacred mountain Parnassus, where they lived muses - 9 sisters, Greek deities, personifying poetic and musical inspiration, patroness of arts and sciences.

Greek muses
|
What patronizes |
Attributes |
|
|
Calliope ("beautifully speaking") |
muse of epic or heroic poetry |
wax tablet and stylos (bronze writing rod) |
|
("Glorifying") |
muse of history |
papyrus scroll or scroll case |
|
("Pleasant") |
muse of love or erotic poetry, lyrics and marriage songs |
kifara (stringed plucked musical instrument, a type of lyre) |
|
("Perfectly enjoyable") |
muse of music and lyric poetry |
avlos (a wind instrument similar to a double-tongued pipe, the predecessor of the oboe) and siringa (a musical instrument, a kind of longitudinal flute) |
|
("Heavenly") |
muse of astronomy |
telescope and sheet with celestial signs |
|
Melpomene ("Singing") |
muse of tragedy |
a wreath of vine leaves or ivy, theatrical gown, tragic mask, sword or mace. |
|
Terpsichore ("Delectable dancing") |
muse of dance |
wreath on the head, lyre and plectrum (mediator) |
|
Polyhymnia ("Singing") |
muse of sacred song, eloquence, lyric, melody and rhetoric |
|
|
("Blooming") |
muse of comedy and bucolic poetry |
comic mask in hands and wreath ivy on my head |
Lower deities in Greek mythology, these are satyrs, nymphs and ora.
Satyrs - (Greek satyroi) - these are forest deities (the same as in Russia devil), demons fertility, retinue of Dionysus. They were depicted as goat-footed, hairy, with horse tails and small horns. Satyrs are indifferent to people, mischievous and cheerful, they were interested in hunting, wine, and chased forest nymphs. Their other hobby is music, but they played only wind instruments that emit sharp, piercing sounds - flute and pipe. In mythology, they personified a coarse, base beginning in nature and man, therefore they were represented with ugly faces - with blunt, wide noses, swollen nostrils, and disheveled hair.

Nymphs - (the name means "source", among the Romans - "bride") the personification of living elemental forces, noticed in the murmur of a stream, in the growth of trees, in the wild beauty of mountains and forests, the spirits of the earth's surface, manifestations of natural forces acting in addition to humans in the solitude of grottoes , valleys, forests, away from cultural centers. They were portrayed as beautiful young girls with wonderful hair, with a dress of wreaths and flowers, sometimes in a dancing pose, with bare legs and arms, with loose hair. They do yarn, weaving, sing songs, dance in the meadows to the flute of Pan, hunt with Artemis, participate in the noisy orgies of Dionysus, and are constantly fighting annoying satyrs. In the view of the ancient Greeks, the world of nymphs was very vast.
The azure pond was full of flying nymphs,
The garden was animated by dryads,
And the bright water spring sparkled from the urn
Laughing naiads.
F. Schiller
Nymphs of the mountains - oreads,
nymphs of forests and trees - dryads,
source nymphs - naiads,
nymphs of the oceans - oceanids,
nymphs of the sea - nerids,
the nymphs of the valleys - hum,
meadow nymphs - limnads.

Ora - the goddesses of the seasons, were in charge of order in nature. The guardians of Olympus, now opening and then closing its cloudy gates. They are called the gatekeepers of heaven. The horses of Helios are harnessed.

There are numerous monsters in many mythologies. In ancient Greek mythology, there were also a lot of them: Chimera, Sphinx, Lernean hydra, Echidna and many others.
In the same vestibule the shadows of monsters are crowded together:
Scyllas are two-shaped here and herds of centaurs live,
Here Briareus the hundred-handed lives, and the dragon from Lernaeus
Topi hisses, and the Chimera frightens enemies with fire,
Harpies in a flock around the three-body giants fly ...
Virgil, "Aeneid"
Harpies - these are evil kidnappers of children and human souls, suddenly swooping in and just as suddenly disappearing like the wind, terrify people. Their number ranges from two to five; depicted in the form of wild half-women, half-birds of a disgusting appearance with wings and paws of a vulture, with long sharp claws, but with the head and chest of a woman.

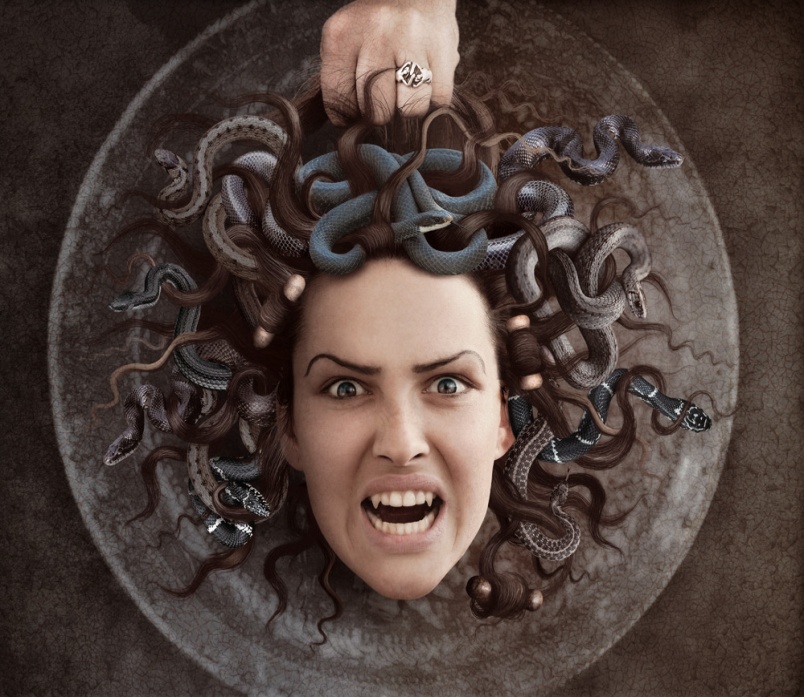
Gorgon Medusa - a monster with a woman's face and snakes instead of hair, whose gaze turned a person to stone. According to legend, she was a beautiful girl with wonderful hair. Poseidon, seeing Medusa and falling in love, seduced her in the temple of Athena, for which the goddess of wisdom, in anger, turned the hair of the Gorgon Medusa into a serpent. The Gorgon Medusa was defeated by Perseus, and her head was placed on the aegis of Athena.

Minotaur - a monster with a human body and a bull's head. Was born of the unnatural love of Pasiphai (wife of King Minos) and a bull. Minos hid a monster in the Knossos labyrinth. Every eight years, 7 young men and 7 girls descended into the labyrinth, intended for the Minotaur as victims. Theseus defeated the Minotaur, and with the help of Ariadne, who gave him a ball of thread, got out of the maze.

Cerberus (Cerberus) - this is a three-headed dog with a serpentine tail and snake heads on its back, it guarded the exit from the kingdom of Hades, not allowing the dead to return to the kingdom of the living. He was defeated by Hercules during one of his exploits.

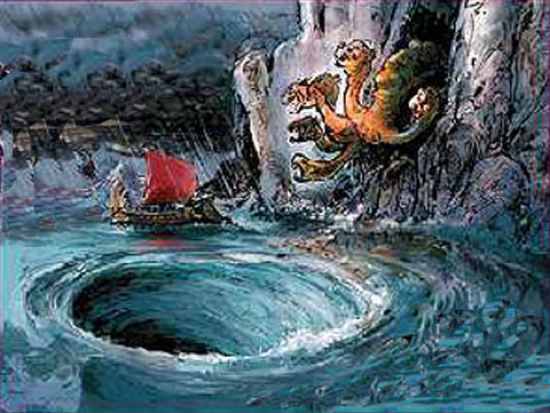
Scylla and Charybdis Are sea monsters located at an arrow flight distance from each other. Charybdis is a sea whirlpool that absorbs and erupts water three times a day. Scylla ("barking") is a monster in the form of a woman, whose lower body was turned into 6 dog heads. When the ship passed the rock where Scylla lived, the monster, gaping all its jaws, kidnapped 6 people from the ship at once. The narrow strait between Scylla and Charybdis was a mortal danger to all who sailed along it.

Also in Ancient Greece, there were other mythical characters.
Pegasus - a winged horse, a favorite of the muses. He flew at the speed of the wind. Riding Pegasus meant getting poetic inspiration. Born at the headwaters of the Ocean, therefore he was named Pegasus (from the Greek. "Stormy current"). According to one version, he jumped out of the body of the gorgon Medusa after Perseus chopped off her head. Pegasus delivered thunder and lightning to Zeus to Olympus from Hephaestus, who made them.
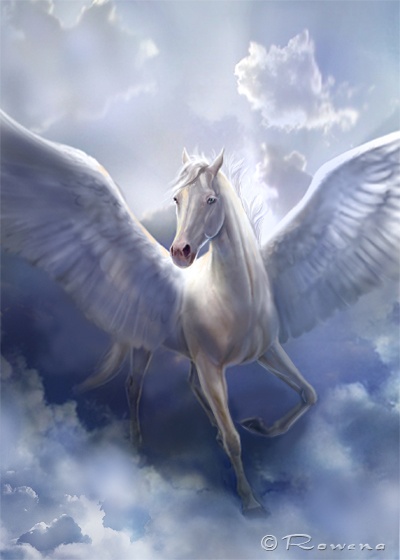

From the foam of the sea, from the azure wave,
Faster than an arrow and more beautiful than a string,
An amazing fairy horse flies
And easily catches the heavenly fire!
He likes to splash in colored clouds
And often walks in magic poetry.
So that the ray of inspiration in the soul does not go out,
Saddle you, snow-white Pegasus!
Unicorn - a mythical creature symbolizing chastity. Usually depicted as a horse with one horn protruding from the forehead. The Greeks believed that the unicorn belongs to Artemis, the goddess of the hunt. Subsequently, in medieval legends, there was a version that only a virgin could tame him. Having caught a unicorn, it can only be restrained by a golden bridle.

Centaurs - wild mortal creatures with the head and torso of a man on the body of a horse, inhabitants of mountains and forest thickets, accompany Dionysus and are distinguished by their violent disposition and intemperance. Presumably, centaurs were originally the embodiment of mountain rivers and turbulent streams. In heroic myths, centaurs are the educators of heroes. For example, Achilles and Jason were raised by the centaur Chiron.
The life of the ancient Greek gods on Mount Olympus seemed to people to be sheer fun and a daily holiday. The myths and legends of those times are a treasure trove of philosophical and cultural knowledge. After examining the list of the gods of Ancient Greece, you can plunge into a completely different world. Mythology surprises with its uniqueness, it is important in that it pushed humanity to the development and emergence of many sciences, such as mathematics, astronomy, rhetoric, logic.
First generation
Initially there was Mist, and from it Chaos arose. From their union, Erebus (darkness), Nikta (night), Uranus (sky), Eros (love), Gaia (earth) and Tartarus (abyss) appeared. All of them played a huge role in the formation of the pantheon. All other deities are somehow connected with them.
Gaia is one of the first deities on earth, which arose along with the sky, sea and air. She is the great mother of everything on earth: the heavenly gods were born from her union with her son Uranus (sky), sea gods from Pontos (sea), giants from Tartaros (hell), and mortal beings are created from her flesh. She was portrayed as an obese woman, half rising from the ground. We can assume that it was she who invented all the names of the gods of Ancient Greece, a list of which can be found below.
Uranus is one of the primeval gods of Ancient Greece. He was the original ruler of the universe. He was overthrown by his son Kronos. Born by one Gaia, he was also her husband. Some sources call his father Akmon. Uranus was depicted as a bronze dome covering the world.
List of the gods of Ancient Greece, born by Uranus and Gaia: Ocean, Kous, Hyperion, Crius, Thea, Rhea, Themis, Iapetus, Mnemosyne, Tethys, Kronos, Cyclops, Brontes, Sterop.
Uranus did not feel much love for his children, or rather, hated them. And after birth, he imprisoned them in Tartarus. But during their uprising, he was defeated and castrated by his son Kronos.
Second generation
The Titans, born of Uranus and Gaia, were the six gods of time. The list of titans of ancient Greece includes:
Ocean - tops the list of the gods of Ancient Greece, titan. It was a large river, surrounding the land, and was the seat of all fresh water. Ocean's wife was his sister, the Titanide Tefida. Their union gave birth to rivers, streams and thousands of oceanids. They did not take part in the titanomachy. The ocean was depicted as a horned bull with a fish's tail instead of legs.
Kei (Koy / Keos) is the brother and husband of Phoebe. Their union gave birth to Leto and Asteria. Depicted as a celestial axis. It was around her that the clouds revolved and Helios and Selena walked across the sky. The couple were thrown by Zeus into Tartarus.
Krios (Krios) is an ice titan capable of freezing all life. He shared the fate of his brothers and sisters, who were thrown into Tartarus.
Iapetus (Iapetus / Iapetus) - the most eloquent, commanded the titans when attacking the gods. Also sent by Zeus to Tartarus.
Hyperion - lived on the island of Trinacria. He did not take part in the titanomachy. His wife was the titinide Thea (thrown into Tartarus together with her brothers and sisters).

Kronos (Chronos / Kronus) is the temporary ruler of the world. He was so afraid of losing the power of the supreme god that he devoured his children so that none of them would claim the throne of the ruler. He was married to his sister Ray. She managed to save one child and hide him from Kronos. Deposed by his only saved heir Zeus and sent to Tartarus.
Closer to people
The next generation is the most famous. They are the main gods of Ancient Greece. The list of their exploits, adventures and legends with their participation is quite impressive.
They not only became closer to people, descending from heaven and emerging from chaos to the top of the mountain. The gods of the third generation began to contact people more often and more willingly.

Zeus especially boasted of this, who was very partial to earthly women. And the presence of the divine wife Hera did not bother him at all. It was from his union with man that the familiar hero of myths, Hercules, was born.
Third generation
These gods dwelt on Mount Olympus. They got their title from her name. There are 12 gods of Ancient Greece, the list of which is known to almost everyone. All of them performed their functions and were endowed with unique talents.

But more often they speak of fourteen gods, the first six of which were the children of Kronos and Rhea:
Zeus - the main god of Olympus, the ruler of the sky, personified power and strength. God of lightning, thunder and creator of people. The main attributes of this god were: Aegis (shield), Labrys (double-sided ax), Zeus's lightning (two-pointed pitchfork with notches) and an eagle. Distributed good and evil. He was in league with several women:
- Metis - the first wife, the goddess of wisdom, was swallowed by her husband;
- Themis is the goddess of justice, the second wife of Zeus;
- Hera - the last wife, the goddess of marriage, was the sister of Zeus.
Poseidon is the god of rivers, floods, seas, drought, horses and earthquakes. His attributes were: a trident, a dolphin and a chariot with white-maned horses. The wife is Amphitrite.
Demeter is the mother of Persephone, sister of Zeus and his beloved. She is the goddess of fertility and patronizes farmers. Demeter's attribute is a wreath of ears.
Hestia is the sister of Demeter, Zeus, Hades, Hera and Poseidon. Patroness of the sacrificial fire and family hearth. Made a vow of chastity. The main attribute was a torch.
Hades is the ruler of the underworld of the dead. Spouse of Persephone (goddess of fertility and queen of the kingdom of the dead). Hades' attributes were a two-pronged or a rod. He was portrayed with the underground monster Cerberus - a three-headed dog who stood guard at the entrance to Tartarus.
Hera is the sister and at the same time the wife of Zeus. The strongest and wisest goddess of Olympus. She was the patroness of family and marriage. Hera's obligatory attribute is a diadem. This decoration is a symbol of the fact that she is the main one on Olympus. She obeyed (sometimes reluctantly) all the main gods of Ancient Greece, the list of which she headed.
The rest of the Olympians
Even though these gods did not have such powerful parents, almost all of them were born of Zeus. Each of them was talented in their own way. And he coped well with his duties.
Ares is the son of Hera and Zeus. God of battles, war and masculinity. He was a lover, then the spouse of the goddess Aphrodite. Ares' companions were Eris (goddess of strife) and Enio (goddess of violent war). The main attributes were: a helmet, a sword, dogs, a burning torch and a shield.
Apollo - the son of Zeus and Leto, was the twin brother of Artemis. God of light, leader of muses, god-healer and predictor of the future. Apollo was very loving, he had many mistresses and lovers. The attributes were: a laurel wreath, a chariot, a bow with arrows and a golden lyre.
Hermes is the son of Zeus and the Pleiades of Maya or Persephone. God of trade, eloquence, dexterity, intelligence, animal husbandry and roads. Patron saint of athletes, merchants, artisans, shepherds, travelers, ambassadors and thieves. He is the personal messenger of Zeus and the escort of the dead to the kingdom of Hades. He taught people to write, trade and bookkeeping. Attributes: winged sandals that allow him to fly, invisible helmet, caduceus (wand adorned with two intertwined serpents).

Hephaestus is the son of Hera and Zeus. God of blacksmithing and fire. I limped on both legs. The wives of Hephaestus are Aphrodite and Aglaya. The attributes of the god were: bellows, pincers, chariot and pilos.
Dionysus is the son of Zeus and the mortal woman Semele. God of vineyards and winemaking, inspiration and ecstasy. Patron saint of the theater. He was married to Ariadne. The attributes of God are: a bowl of wine, a vine wreath, and a chariot.
Artemis is the daughter of Zeus and the goddess Leto, the twin sister of Apollo. The young goddess is a hunter. Having been born first, she helped her mother give birth to Apollo. Chaste. Artemis' attributes: doe, quiver of arrows, and chariot.
Demeter is the daughter of Kronos and Rhea. Mother of Persephone (wife of Hades), sister of Zeus and his beloved. Goddess of agriculture and fertility. The Demeter attribute is a wreath of ears.
Athena, daughter of Zeus, completes our list of the gods of Ancient Greece. She was born from his head after he swallowed her mother Themis. Goddess of war, wisdom and craft. Patroness of the Greek city of Athens. Her attributes were: a shield with the image of the Gorgon Medusa, an owl, a snake and a spear.
Born in the foam?
I would like to talk about the next goddess separately. She is not only a symbol of female beauty to this day. In addition, the story of its origin is hidden in secret.
There are many controversies and assumptions about the birth of Aphrodite. The first version: the goddess was born from the seed and blood of Uranus castrated by Kronos, which fell into the sea and formed foam. Second version: Aphrodite emerged from a sea shell. The third hypothesis: she is the daughter of Dione and Zeus.
This goddess was in charge of beauty and love. Spouses: Ares and Hephaestus. Attributes: chariot, apple, rose, mirror and dove.
How they lived on the great Olympus
All the Olympic gods of Ancient Greece, the list of which you see above, had the right to live and spend all their free time from miracles on the great mountain. The relationship between them was not always rosy, but few of them dared to open hostility, knowing the power of their opponent.

Even among the great divine creatures, there was no permanent peace. But everything was decided by intrigues, secret conspiracies and betrayals. It is very similar to the human world. And this is understandable, because humanity was created precisely by the gods, so they all look like us.
Gods who do not live on top of Olympus
Not all deities had a chance to reach such heights and climb Mount Olympus to rule the world there, feasting and having fun. Many other gods either could not deserve such a high honor, or were humble and content with ordinary life. If, of course, you can call that the existence of a deity. In addition to the Olympian gods, there were other gods of Ancient Greece, the list of their names is here:
- Hymenaeus is the god of marriage bonds (son of Apollo and the muse Calliope).
- Nika is the goddess of victory (daughter of Styx and the titan Pallant).
- Irida is the goddess of the rainbow (daughter of the sea god Tavmant and the oceanis of Electra).
- Ata is the goddess of the darkening of the mind (daughter of Zeus).
- Apata is the lady of lies (heiress of the goddess of night darkness Nyukta).
- Morpheus is the god of dreams (the son of the lord of dreams, Hypnos).
- Phobos is the god of fear (a descendant of Aphrodite and Ares).
- Deimos is the lord of terror (son of Ares and Aphrodite).
- Ora are the goddesses of the seasons (daughters of Zeus and Themis).
- Aeolus is the demigod of the winds (heir to Poseidon and Arna).
- Hecate is the mistress of darkness and all monsters (the result of the union of the titan Persian and Asteria).
- Thanatos is the god of death (son of Erebus and Nyukta).
- Erinias are the goddess of revenge (daughters of Erebus and Nyukta).
- Pontus is the ruler of the inner sea (heir to Ether and Gaia).
- Moira - goddess of fate (daughter of Zeus and Themis).

These are not all the gods of Ancient Greece, the list of which can be continued even further. But to get acquainted with the main myths and legends, it is enough to know only these characters. If you want to read more stories about each, we are sure that the ancient storytellers came up with a lot of interweaving of their destinies and details of the divine life, in which you will gradually get acquainted with more and more new heroes.
The meaning of Greek mythology
There were also muses, nymphs, satyrs, centaurs, heroes, cyclops, giants and monsters. This whole huge world was not invented in one day. Myths and legends have been written for decades, with each retelling acquiring other details and previously unheard of characters. More and more gods of Ancient Greece appeared, the list of whose names grew from one storyteller to another.
The main goal of these stories was to teach future generations the wisdom of elders, to tell in understandable language about good and evil, about honor and cowardice, about loyalty and lies. And besides, such a huge pantheon made it possible to explain almost any natural phenomenon, for which there was no scientific justification yet.

