Cylinder
Def. A cylinder is a body that consists of two circles, superimposed
parallel translation and all line segments connecting the corresponding points
these circles.
The circles are called the bases of the cylinder, and the segments connecting the corresponding points of the circles of these circles are called the generatrices of the cylinder (Fig. 1)



fig. 1 fig. 2 fig. 3 fig. 4
Cylinder properties:
1) The bases of the cylinder are equal and lie in parallel planes.
2) The generatrices of the cylinder are equal and parallel.
Def. The radius of a cylinder is the radius of its base.
Def. The height of a cylinder is the distance between the planes of its bases.
Def. The section of the cylinder by a plane passing through the axis of the cylinder is called the axial section.
The axial section of the cylinder is a rectangle with sides 2R and l(in a straight cylinder l \u003d H) fig. 2
The section of the cylinder, parallel to its axis, are rectangles (Fig. 3).
 Section of a cylinder by a plane parallel to the bases - a circle equal to the bases (Fig. 4)
Section of a cylinder by a plane parallel to the bases - a circle equal to the bases (Fig. 4)
Cylinder surface area.
The lateral surface of the cylinder is composed of generatrices.
The full surface of the cylinder consists of bases and a side surface.
S full = 2 S main + S side ; S main = P ∙ R 2 ; S side = 2 P ∙ R ∙ NS full \u003d 2PR ∙(R + H)
Practical part:
№1. The radius of the cylinder is 3cm, and its height is 5cm. Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe axial section and the area of \u200b\u200bthe floor
surface of the cylinder.
№2.
The diagonal of the axial section of the cylinder is inclined to the base plane at an angle  and is equal to 20 cm. Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder.
and is equal to 20 cm. Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder.
№3. The radius of the cylinder is 2cm, and its height is 3cm. Find the diagonal of the axial section of the cylinder.
№4.
Diagonal of the axial section of the cylinder, equal to  , forms an angle with the base plane
, forms an angle with the base plane  ... Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder.
... Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder.
№5.
The lateral surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder is 15  ... Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe axial section.
... Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe axial section.
№6.
Find the height of the cylinder if its base area is 1 and S side \u003d  .
.
№7.
The diagonal of the axial section of the cylinder has a length of 8 cm and is inclined to the base plane at an angle  ... Find the complete surface of the cylinder.
... Find the complete surface of the cylinder.
The cylindrical chimney with a diameter of 65cm has a height of 18m. How much tin is needed to make it if 10% of the material is spent on the rivet?
Cylinder (ancient Greek. κύλινδρος - roller, roller) - a geometric body bounded by a cylindrical surface and two parallel planes intersecting it. A cylindrical surface is a surface obtained by such a translational motion of a straight line (generatrix) in space that the selected point of the generatrix moves along a plane curve (guideline). The part of the cylinder surface bounded by the cylindrical surface is called the lateral surface of the cylinder. The other part, limited by parallel planes, is the base of the cylinder. Thus, the border of the base will coincide in shape with the guide.
In most cases, a cylinder means a straight circular cylinder, in which the guide is a circle and the bases are perpendicular to the generatrix. Such a cylinder has an axis of symmetry.
Other types of cylinder - (by the slope of the generatrix) oblique or inclined (if the generatrix does not touch the base at a right angle) (in the form of the base) elliptic, hyperbolic, parabolic.
A prism is also a type of cylinder - with a polygon base.
Cylinder surface area
Side surface area

Calculating the lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ba cylinder
The area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder is equal to the length of the generatrix, multiplied by the perimeter of the section of the cylinder by the plane perpendicular to the generatrix.
The lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ba straight cylinder is calculated from its sweep. The unfolded cylinder is a rectangle with a height and length equal to the base perimeter. Consequently, the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder is equal to the area of \u200b\u200bits sweep and is calculated by the formula:
In particular, for a straight circular cylinder:
andFor an inclined cylinder, the lateral surface area is equal to the length of the generatrix, multiplied by the perimeter of the section perpendicular to the generatrix:
Unfortunately, there is no simple formula expressing the lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ban oblique cylinder through the parameters of the base and height, unlike the volume.
Total surface area
The total surface area of \u200b\u200ba cylinder is equal to the sum of the areas of its lateral surface and its bases.
For a straight circular cylinder:
Cylinder volume
There are two formulas for an inclined cylinder:
where is the length of the generator, and is the angle between the generator and the plane of the base. For straight cylinder.For a straight cylinder, and, and the volume is:
For a circular cylinder:
where d - base diameter.
Notes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Synonyms:See what "Cylinder" is in other dictionaries:
- (lat. cylindrus) 1) a geometrical body, bounded from the ends by two circles, from the sides by a plane enveloping these circles. 2) in watchmaking: a special kind of double wheel lever. 3) a hat shaped like a cylinder. Dictionary of foreign words, ... ... Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language
cylinder - a, m. cylindre m., German. Zylinder, lat. cylindrus c. 1. Geometric body formed by the rotation of a rectangle around one of its sides. Cylinder volume. BASS 1. The thickness of the cylinder is equal to the area of \u200b\u200bits base multiplied by the height. Dahl ... Historical Dictionary of Russian Gallicisms
Husband., Greek. straight stack, shaft; blaze, blaze; a body bounded at the ends by two circles, and at the sides by a plane curved in circles. The thickness of the cylinder is equal to the area of \u200b\u200bits base multiplied by the height, geom. Steam cylinder, freebie, pipe in which ... ... Dahl's Explanatory Dictionary - a tall men's hat made of silk plush with a small hard brim ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
CYLINDER, a solid or surface formed by rotating a rectangle around one of its sides as an axis. The volume of the cylinder, if we denote its height as h, and the radius of the base as r, is equal to pr2h, and the area of \u200b\u200bthe curved surface is 2prh ... Scientific and technical encyclopedic dictionary
CYLINDER, cylinder, husband. (from the Greek kylindros). 1. A geometric body formed by the rotation of a rectangle about one of its sides, called an axis, and having a circle at its bases (mat.). 2. Part of machines (motors, pumps, compressors, etc.) in ... ... Ushakov's Explanatory Dictionary
CYLINDER, ah, husband. 1. A geometric body formed by rotating a rectangle around one of its sides. 2. Column-shaped object, eg. part of a piston machine. 3. A tall hard hat of this shape with small brim. Black c. | adj. ... ... Ozhegov's Explanatory Dictionary
- (Steam cylinder) is one of the main parts of piston machines. It is carried out in the form of a hollow round cylinder, in which the piston moves. Central heating of steam engines is usually supplied with a steam jacket for heating its walls in order to reduce steam condensation. ... ... Marine dictionary
The name of the science "geometry" is translated as "measurement of the earth". It was born through the efforts of the very first ancient land surveyors. And it was like this: during the floods of the sacred Nile, streams of water sometimes washed away the boundaries of farmers' plots, and the new boundaries might not coincide with the old ones. Taxes were paid by the peasants to the pharaoh's treasury in proportion to the size of the land allotment. After the spill, special people were involved in measuring the arable land in the new borders. It was as a result of their activities that a new science arose, which was developed in Ancient Greece. There she received the name and acquired an almost modern look. Later, the term became the international name for the science of flat and volumetric figures.
Planimetry is a branch of geometry that deals with the study of plane figures. Another branch of science is stereometry, which examines the properties of spatial (volumetric) figures. The cylinder described in this article also belongs to such shapes.
There are plenty of examples of the presence of cylindrical objects in everyday life. Almost all parts of rotation - shafts, bushings, journals, axles, etc. have a cylindrical (much less often - conical) shape. The cylinder is widely used in construction: towers, support, decorative columns. And besides, dishes, some types of packaging, pipes of various diameters. And finally - the famous hats, which have become a symbol of male elegance for a long time. The list is endless.
Defining a cylinder as a geometric figure
A cylinder (circular cylinder) is usually called a figure consisting of two circles, which, if desired, are combined using a parallel transfer. It is these circles that are the bases of the cylinder. But the lines (straight line segments) connecting the corresponding points are called "generators".
It is important that the bases of the cylinder are always equal (if this condition is not met, then we have a truncated cone in front of us, something else, but not a cylinder) and are in parallel planes. The segments connecting the corresponding points on the circles are parallel and equal.
The set of an infinite set of generators is nothing more than the lateral surface of the cylinder - one of the elements of this geometric figure. Another important component is the circles discussed above. They are called bases.
Types of cylinders
The simplest and most common type of cylinder is circular. It is formed by two regular circles that act as bases. But there may be other figures instead.

The bases of cylinders can form (except for circles) ellipses, other closed shapes. However, the cylinder may not necessarily have a closed shape. For example, the base of a cylinder can be a parabola, hyperbola, or another open function. Such a cylinder will be open or expanded.
On the angle of inclination of generatrices to the bases, the cylinders can be straight or inclined. For a straight cylinder, the generatrices are strictly perpendicular to the base plane. If this angle differs from 90 °, the cylinder is inclined.

What is a surface of revolution
The straight circular cylinder is without doubt the most common surface of revolution used in engineering. Sometimes, for technical reasons, conical, spherical, some other types of surfaces are used, but 99% of all rotating shafts, axles, etc. made precisely in the form of cylinders. In order to better understand what a surface of revolution is, we can consider how the cylinder itself is formed.
Let's say there is a certain straight line alocated vertically. ABCD - a rectangle, one of the sides of which (segment AB) lies on a straight line a... If you rotate a rectangle around a straight line, as shown in the figure, the volume that it will occupy while rotating will be our body of revolution - a straight circular cylinder with height H \u003d AB \u003d DC and radius R \u003d AD \u003d BC.

In this case, as a result of the rotation of the shape - the rectangle - a cylinder is obtained. By rotating a triangle, you can get a cone, rotating a semicircle - a ball, etc.
Cylinder surface area
In order to calculate the surface area of \u200b\u200ban ordinary right circular cylinder, it is necessary to calculate the areas of the bases and the lateral surface.

First, consider how the lateral surface area is calculated. This is the product of the circumference and the height of the cylinder. The circumference, in turn, is equal to twice the product of the universal number P by the radius of the circle.
The area of \u200b\u200ba circle is known to be equal to the product P per square of radius. So, adding up the formulas for the area of \u200b\u200bdetermining the lateral surface with a doubled expression for the area of \u200b\u200bthe base (there are two of them) and making simple algebraic transformations, we get the final expression for determining the surface area of \u200b\u200ba cylinder.
Determining the volume of a figure
The volume of a cylinder is determined according to the standard scheme: the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe base is multiplied by the height.

Thus, the final formula looks like this: the desired one is defined as the product of the body height by the universal number Pand by the square of the base radius.
The resulting formula, I must say, is applicable to solving the most unexpected problems. In the same way as the volume of a cylinder, for example, the volume of the electrical wiring is determined. This is sometimes necessary to calculate the mass of the wires.

The only differences in the formula are that instead of the radius of one cylinder, the diameter of the wire core is divided in half, and the number of cores in the wire appears in the expression N... Also, the length of the wire is used instead of the height. Thus, the volume of the "cylinder" is calculated not by one, but by the number of braided wires.
Such calculations are often required in practice. After all, a significant part of the water tanks are made in the form of a pipe. And it is often necessary to calculate the volume of a cylinder even in a household.
However, as already mentioned, the shape of the cylinder can be different. And in some cases it is required to calculate what the volume of an inclined cylinder is equal to.
The difference is that the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe base is multiplied not by the length of the generatrix, as in the case of a straight cylinder, but by the distance between the planes - a perpendicular segment built between them.

As can be seen from the figure, such a segment is equal to the product of the length of the generator and the sine of the angle of inclination of the generator to the plane.
How to build a cylinder unfolded
In some cases, it is required to cut out a cylinder sweep. The figure below shows the rules by which a blank is built for the manufacture of a cylinder with a given height and diameter.

It should be borne in mind that the figure is shown without taking into account the seams.
Beveled cylinder differences

Let us imagine a certain straight cylinder bounded on one side by a plane perpendicular to the generatrix. But the plane that bounds the cylinder on the other hand is not perpendicular to the generatrix and is not parallel to the first plane.

The figure shows a beveled cylinder. Plane and at a certain angle other than 90 ° to the generators, it intersects the figure.
This geometric shape is more common in practice in the form of pipe joints (elbows). But there are even buildings built in the form of a beveled cylinder.
Beveled cylinder geometry

The inclination of one of the planes of the beveled cylinder slightly changes the order in which both the surface area of \u200b\u200bsuch a figure and its volume are calculated.
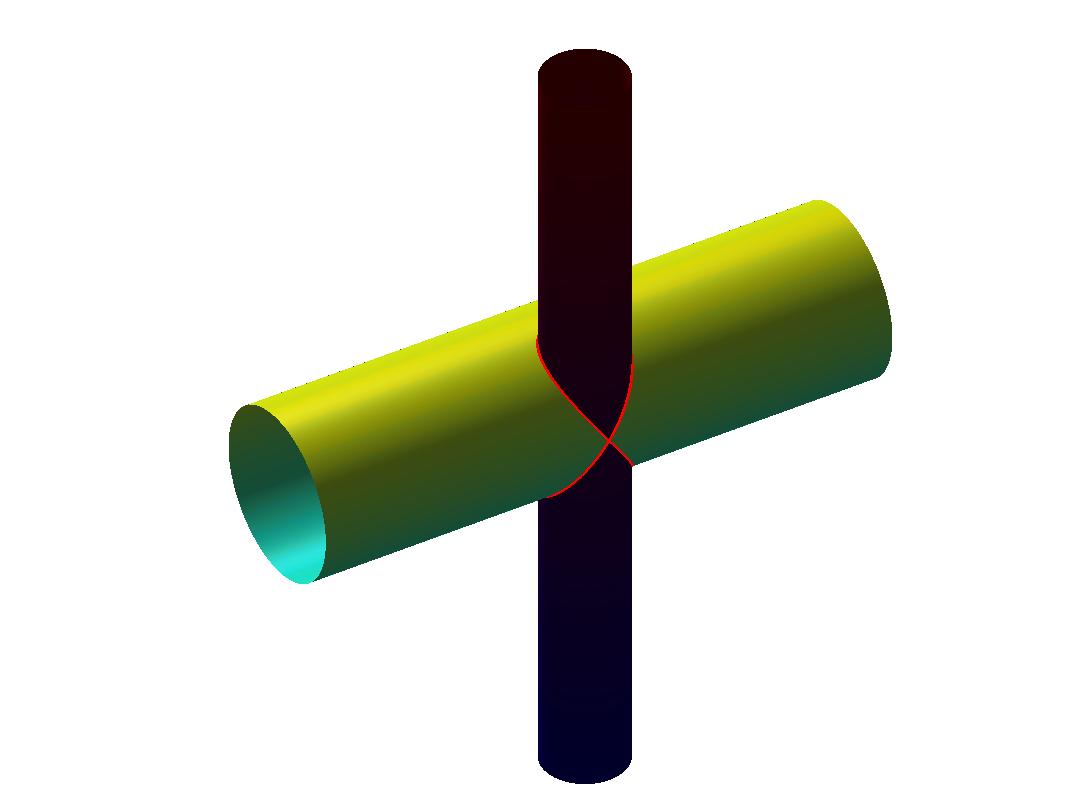
Bounded by a cylindrical surface and two parallel planes intersecting it.
Related definitions
Cylindrical surface - the surface obtained by moving a straight line (generatrix), parallel to any given, intersecting a curved line (guide), lying in a non-parallel given straight plane. Plane figures formed by the intersection of a cylindrical surface with two parallel planes are called cylinder bases... The cylindrical surface between the planes of the bases is called lateral surface cylinder. If the plane of the base is parallel to the plane of the guide, the border of the base will coincide in shape with the guide.
Types
In most cases, a cylinder means a straight circular cylinder, in which the guide is a circle and the bases are perpendicular to the generatrix. Such a cylinder has an axis of symmetry.
Other types of cylinder - (by the slope of the generatrix) oblique or inclined (if the generatrix does not touch the base at a right angle) (in the form of the base) elliptic, hyperbolic, parabolic.
A prism is also a type of cylinder - with a polygon base.
Cylinder surface area
Side surface area
 The area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder is equal to the length of the generatrix, multiplied by the perimeter of the section of the cylinder by the plane perpendicular to the generatrix.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder is equal to the length of the generatrix, multiplied by the perimeter of the section of the cylinder by the plane perpendicular to the generatrix.
The lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ba straight cylinder is calculated from its sweep. A cylinder unfolded is a rectangle with a height and length equal to the perimeter of the base. Consequently, the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the cylinder is equal to the area of \u200b\u200bits sweep and is calculated by the formula:
In particular, for a straight circular cylinder:
and
For an inclined cylinder, the lateral surface area is equal to the length of the generatrix, multiplied by the perimeter of the section perpendicular to the generatrix:
Unlike the volume, there is no simple formula expressing the lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ban oblique cylinder through the parameters of the base and height. For an oblique circular cylinder, you can use the approximate formulas for the perimeter of an ellipse, and then multiply the resulting value by the length of the generatrix.
Total surface area
The total surface area of \u200b\u200ba cylinder is equal to the sum of the areas of its lateral surface and its bases.
For a straight circular cylinder:
Cylinder volume
 There are two formulas for an inclined cylinder:
There are two formulas for an inclined cylinder:
- The volume is equal to the length of the generatrix multiplied by the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder by the plane perpendicular to the generatrix. ,
- The volume is equal to the area of \u200b\u200bthe base, multiplied by the height (the distance between the planes in which the bases lie): ,
For straight cylinder , and , and the volume is:
For a circular cylinder:
where d - base diameter.
Write a review on the article "Cylinder"
Notes
Excerpt from the Cylinder
- Paris la capitale du monde ... [Paris is the capital of the world ...] - Pierre said, finishing his speech.The captain looked at Pierre. He had a habit in the middle of a conversation to stop and look with intently laughing, affectionate eyes.
- Eh bien, si vous ne m "aviez pas dit que vous etes Russe, j" aurai parie que vous etes Parisien. Vous avez ce je ne sais, quoi, ce ... [Well, if you hadn’t told me that you are Russian, I would have bet that you were Parisian. There is something in you, this ...] - and, having said this compliment, he again silently looked.
- J "ai ete a Paris, j" y ai passe des annees, [I was in Paris, I spent whole years there,] - said Pierre.
- Oh ca se voit bien. Paris! .. Un homme qui ne connait pas Paris, est un sauvage. Un Parisien, ca se sent a deux lieux. Paris, s "est Talma, la Duschenois, Potier, la Sorbonne, les boulevards, - and noticing that the conclusion is weaker than the previous one, he hastily added: - Il n" ya qu "un Paris au monde. Vous avez ete a Paris et vous etes reste Busse. Eh bien, je ne vous en estime pas moins. [Oh, you can see it. Paris! .. A man who does not know Paris is a savage. You can recognize a Parisian two miles away. Paris is Talma, Duchenois, Potier, Sorbonne, boulevards ... There is one Paris all over the world. You were in Paris and remained Russian. Well, I respect you no less for that.]
Under the influence of the wine he had drunk and after days spent in solitude with his gloomy thoughts, Pierre felt involuntary pleasure in talking with this cheerful and good-natured man.
- Pour en revenir a vos dames, on les dit bien belles. Quelle fichue idee d "aller s" enterrer dans les steppes, quand l "armee francaise est a Moscou. Quelle chance elles ont manque celles la. Vos moujiks c" est autre chose, mais voua autres gens civilises vous devriez nous connaitre mieux que ca ... Nous avons pris Vienne, Berlin, Madrid, Naples, Rome, Varsovie, toutes les capitales du monde ... On nous craint, mais on nous aime. Nous sommes bons a connaitre. Et puis l "Empereur! [But back to your ladies: they say they are very beautiful. What a stupid idea to go to bury yourself in the steppe when the French army is in Moscow! They missed a wonderful opportunity. Your men, I understand, but you are people educated - should have known us better than this. We took Vienna, Berlin, Madrid, Naples, Rome, Warsaw, all the capitals of the world. They are afraid of us, but they love us. It is not harmful to know us better. And then the emperor ...] - he began, but Pierre interrupted him.
- L "Empereur," repeated Pierre, and his face suddenly caught a sad and embarrassed expression. - Est ce que l "Empereur? .. [Emperor ... What an emperor? ..]
- L "Empereur? C" est la generosite, la clemence, la justice, l "ordre, le genie, voila l" Empereur! C "est moi, Ram ball, qui vous le dit. Tel que vous me voyez, j" etais son ennemi il y a encore huit ans. Mon pere a ete comte emigre ... Mais il m "a vaincu, cet homme. Il m" a empoigne. Je n "ai pas pu resister au spectacle de grandeur et de gloire dont il couvrait la France. Quand j" ai comprised ce qu "il voulait, quand j" ai vu qu "il nous faisait une litiere de lauriers, voyez vous, je me suis dit: voila un souverain, et je me suis donne a lui. Eh voila! Oh, oui, mon cher, c "est le plus grand homme des siecles passes et a venir. [Emperor? This generosity, mercy, justice, order, genius - that's what an emperor is! It is I, Rambal, I am telling you. As you see me, I was his enemy eight years ago. My father was a count and an emigrant. But he defeated me, this man. He took possession of me. I could not resist the spectacle of greatness and glory with which he covered France. When I realized what he wanted, when I saw that he was preparing a bed of laurels for us, I said to myself: here is the sovereign, and I surrendered to him. And so! Oh yes, my dear, this is the greatest man of past and future centuries.] kýlindros, roller, roller) - a geometric body bounded by a cylindrical surface (called the lateral surface of the cylinder) and no more than two surfaces (cylinder bases); moreover, if there are two bases, then one is obtained from the other by parallel transfer along the generatrix of the lateral surface of the cylinder; and the base intersects each generatrix of the lateral surface exactly once.
An infinite body bounded by a closed infinite cylindrical surface is called endless cylinderbounded by a closed cylindrical ray and its base is called open cylinder... The base and generatrices of a cylindrical beam are called respectively the base and generatrices of an open cylinder.
A finite body, bounded by a closed finite cylindrical surface and two sections that distinguished it, is called end cylinder, or actually cylinder... The sections are called the bases of the cylinder. By the definition of a finite cylindrical surface, the bases of the cylinder are equal.
Obviously, the generatrices of the lateral surface of the cylinder are equal in length (called height cylinder) segments lying on parallel straight lines, and their ends lying on the bases of the cylinder. Mathematical curiosities include the definition of any finite three-dimensional surface without self-intersections as a cylinder of zero height (this surface is considered simultaneously both bases of the final cylinder). The bases of the cylinder have a qualitative effect on the cylinder.
If the bases of the cylinder are flat (and, therefore, the planes containing them are parallel), then the cylinder is called standing on a plane... If the bases of a cylinder standing on a plane are perpendicular to the generatrix, then the cylinder is called straight.
In particular, if the base of a cylinder standing on a plane is a circle, then we speak of a circular (round) cylinder; if ellipse - then elliptical.
The volume of the final cylinder is equal to the integral of the base area along the generatrix. In particular, the volume of a straight circular cylinder is
(where is the radius of the base, is the height).
The lateral surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder is calculated using the following formula:
The total surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder is the sum of the lateral surface area and the base area. For a straight circular cylinder:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what "Cylinder (geometry)" is in other dictionaries:
A branch of mathematics dealing with the study of the properties of various shapes (points, lines, angles, two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects), their size and relative position. For the convenience of teaching, geometry is subdivided into planimetry and solid geometry. AT… … Collier's Encyclopedia
- (γήμετρώ earth, μετρώ meru). The concepts of space, position and form are among the original concepts with which man was already familiar in ancient times. The first steps in Georgia were taken by the Egyptians and Chaldeans. In Greece, G. was introduced ... ... Encyclopedic Dictionary of F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron
FREE SURFACE GEOMETRY - the shape of the free surface, formed under the action of gravity and centrifugal force when the liquid metal rotates around the axis of rotation. With a horizontal axis of rotation, the free surface is a circular cylinder, with a vertical ... Metallurgical Dictionary
A section of geometry in which geometric images are studied by methods of mathematical analysis. The main objects of differential geometry are arbitrary sufficiently smooth curves (lines) and surfaces of Euclidean space, as well as families of lines and ...
This term has other meanings, see Pyramidatsu (meanings). The credibility of this section of the article has been questioned. You must verify the accuracy of the facts in this section. There may be explanations on the discussion page ... Wikipedia
A theory that studies external geometry and the relationship between external and internal. geometry of submanifolds of Euclidean or Riemannian space. P. m. Is a generalization of the classic. differential geometry of surfaces in Euclidean space. ... ... Encyclopedia of Mathematics
Cartesian coordinate system Analytical geometry is a section of geometry in which ... Wikipedia
Section of geometry, in which geometrical are studied. images, primarily curves and surfaces, by methods of mathematical. analysis. Usually, differential geometry studies the properties of curves and surfaces in the small, that is, the properties of arbitrarily small pieces of them. Besides, in … Encyclopedia of Mathematics
This term has other meanings, see Scope (meanings). Volume is an additive function of the set (measure), which characterizes the capacity of the area of \u200b\u200bspace that it occupies. Originally arose and was applied without strict ... ... Wikipedia
The part of geometry that is part of elementary mathematics (See Elementary Mathematics). The boundaries of e. G., As well as of elementary mathematics in general, are not strictly delineated. They say that E. g. Is that part of geometry that is studied in ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
Books
- Geometry. 10-11 grades. Technological maps of lessons (CD). FSES, Gilyarova Marina Gennadievna. An interactive whiteboard in high school lessons is an electronic modern tool that significantly speeds up access to necessary information, facilitates its perception and contributes to ...
