Fig, fig, fig tree - these are all names of the same plant, which we strongly associate with Mediterranean life. Anyone who has ever tasted fig fruits knows how delicious it is. But, in addition to a delicate sweet taste, they are also very healthy. And here is an interesting detail: it turns out that figs are a completely unpretentious plant. In addition, it can be successfully grown on a plot in the middle lane or in a house - in a container.
Quite often, even experienced summer residents face difficulties in growing tomato seedlings. For some, all seedlings turn out to be elongated and weak, for others, they suddenly begin to fall and die. The thing is that it is difficult to maintain in an apartment ideal conditions for growing seedlings. Seedlings of any plants need to provide a lot of light, sufficient humidity and optimal temperature. What else do you need to know and observe when growing tomato seedlings in an apartment?
Delicious vinaigrette with apple and sauerkraut - a vegetarian salad of boiled and chilled, raw, pickled, salted, pickled vegetables and fruits. The name comes from a French sauce made from vinegar, olive oil and mustard (vinaigrette). Vinaigrette appeared in Russian cuisine not so long ago, around the beginning of the 19th century, perhaps the recipe was borrowed from Austrian or German cuisine, since the ingredients for the Austrian herring salad are very similar.
When we dreamily touch bright seed bags in our hands, we are sometimes subconsciously sure that we have a prototype of the future plant. We mentally allocate a place for him in the flower garden and look forward to the cherished day of the appearance of the first bud. However, buying seeds does not always guarantee that you will eventually get the desired flower. I would like to draw attention to the reasons why the seeds may not sprout or die at the very beginning of germination.
Spring is coming, and gardeners have more work to do, and with the onset of heat, changes in the garden are happening rapidly. Buds are already beginning to swell on plants that were still sleeping yesterday, everything literally comes to life before our eyes. After a long winter, this can not but rejoice. But along with the garden, its problems come to life - pests and pathogens. Weevils, flower beetles, aphids, clasterosporiasis, maniliasis, scab, powdery mildew- the list can be very long.
Breakfast toast with avocado and egg salad is a great start to the day. The egg salad in this recipe acts as a thick sauce seasoned with fresh vegetables and shrimp. My egg salad is quite unusual, it is a dietary version of everyone's favorite snack - with Feta cheese, Greek yogurt and red caviar. If you have time in the morning, never deny yourself the pleasure of cooking something tasty and healthy. The day should start with positive emotions!
Perhaps every woman at least once received a gift blooming orchid. It is not surprising, because such a lively bouquet looks amazing and blooms for a long time. Orchids cannot be called very difficult indoor crops to grow, but not fulfilling the main conditions for their maintenance often leads to the loss of a flower. If you are just getting started with indoor orchids, you should find out the correct answers to the main questions on growing these beautiful plants in the house.
Lush cheesecakes with poppy seeds and raisins, prepared according to this recipe, in my family they eat it in the blink of an eye. Moderately sweet, plump, tender, with an appetizing crust, without excess oil, in a word, just like mother or grandmother fried in childhood. If the raisins are very sweet, then granulated sugar can not be added at all, without sugar, cheesecakes will be better fried and will never burn. Cook them in a well-heated frying pan, greased with oil, over low heat and without a lid!
Cherry tomatoes differ from their large counterparts not only in the small size of the berries. Many varieties of cherry are characterized by a unique sweet taste, which is very different from the classic tomato. Anyone who has never tasted such cherry tomatoes with their eyes closed may well decide that they are tasting some unusual Exotic fruits. In this article, I will talk about five different cherry tomatoes that have the sweetest fruits of unusual colors.
I started growing annual flowers in the garden and on the balcony more than 20 years ago, but I will never forget my first petunia, which I planted in the country along the path. Only a couple of decades have passed, but one wonders how different petunias of the past are from today's many-sided hybrids! In this article, I propose to trace the history of the transformation of this flower from a simpleton into a real queen of annuals, as well as consider modern varieties of unusual colors.
Salad with spicy chicken, mushrooms, cheese and grapes - fragrant and satisfying. This dish can be served as a main dish if you are preparing a cold dinner. Cheese, nuts, mayonnaise are high-calorie foods, combined with spicy fried chicken and mushrooms, you get a very nutritious snack that is refreshed by sweet and sour grapes. The chicken fillet in this recipe is marinated in a spicy mixture of ground cinnamon, turmeric and chili powder. If you like food with a spark, use hot chili.
The question of how to grow healthy seedlings is a concern for all summer residents in early spring. It seems that there are no secrets here - the main thing for fast and strong seedlings is to provide them with warmth, moisture and light. But in practice, in a city apartment or a private house, this is not so easy to do. Certainly, everyone experienced gardener there is a proven way to grow seedlings. But today we will talk about a relatively new assistant in this matter - the propagator.
The variety of tomato "Sanka" is one of the most popular in Russia. Why? The answer is simple. He is the very first to bear fruit in the garden. Tomatoes ripen when other varieties have not even faded yet. Of course, if you follow the recommendations for growing and make an effort, even a novice grower will get a rich harvest and joy from the process. And so that efforts are not in vain, we advise you to plant high-quality seeds. For example, such as seeds from TM "Agrosuccess".
The task of indoor plants in the house is to decorate the house with its appearance, to create a special atmosphere of comfort. For this we are ready to take care of them regularly. Care is not only watering on time, although this is also important. It is necessary to create other conditions: suitable lighting, humidity and air temperature, make the correct and timely transplant. For experienced flower growers there is nothing supernatural in this. But beginners often face certain difficulties.
Tender cutlets from chicken breast with champignons to cook simply according to this recipe with step by step photos. There is an opinion that it is difficult to cook juicy and tender cutlets from chicken breast, this is not so! Chicken meat contains practically no fat, which is why it is dry. But if you add to chicken fillet cream, white bread and mushrooms with onions, you get awesome tasty cutlets that will appeal to both children and adults. IN mushroom season try adding wild mushrooms to the minced meat.
Pruning trees is a mandatory procedure that is known to any experienced gardener. Each fruit plant requires careful and continuous care. Only under such circumstances will it produce a rich and healthy harvest. Fruit trees such as pear, apple and stone fruits need pruning. They are quite demanding in this process. So why should fruit plants be cut in the garden?
Benefits of the procedure
Here's what pruning fruit trees gives:
- crown formation;
- fruiting and growth;
- limiting the size and scope of the crown;
- solution of the phytosanitary problem - the organization of conditions that will be unfavorable for diseases and pests.
 As you can see, with the help of this procedure, gardeners solve many problems at the same time. In addition, the pruning procedure leads to a bountiful harvest and prolongs the life of plants.
As you can see, with the help of this procedure, gardeners solve many problems at the same time. In addition, the pruning procedure leads to a bountiful harvest and prolongs the life of plants.
If not enough light enters the crown and inside it, then the branches located inside do not have the opportunity to bear fruit and die off over time. Fruits are formed only on those tree branches that are exposed to light.
If the crown was not pruned at all or was rarely done, then the fruits will be located on hard-to-reach branches, which are mostly high.
Due to the trimming procedure, the crowns are formed correctly. This, in turn, leads to the active growth of side branches, which makes it possible receive large quantity fruits available places.
Fruit shaping during specific season will depend on the following points:
- from the goal that the gardener wants to achieve;
- from the climatic conditions of the location of the garden in which the planted plant grows;
- on the type of particular culture.
Pruning fruit trees in autumn
This procedure directly depends on the climate in which a particular tree grows. The following subtleties should be taken into account:

Pruning in winter
 In the southern regions of Russia, pruning can be done even in winter. This is explained by the fact that the frosts in the south are much milder, as in the northern regions.
In the southern regions of Russia, pruning can be done even in winter. This is explained by the fact that the frosts in the south are much milder, as in the northern regions.
Winter pruning is done first in order to rejuvenate old trees and give the crown the correct shape of young seedlings.
In addition, winter pruning is often done to reduce the fruiting of young crops. Gardeners know that those specimens in the garden that give abundant harvests in a row for 2-3 years need to be allowed to rest.
From high level harvest, the thin branches of a young tree may well break. In this regard, it is important to cut off excess branches in winter. In the cold season, gardeners subject the crown-forming procedures first to pome breeds, and then to stone fruits.
The ideal dimensions for fruiting plants are as follows: 3 meters high and 3 meters wide. They will make it possible to harvest the bulk of the crop without the use of ladders or stepladders.
Summer processing
 Some believe that summer is the best time to process trees. But in our case, we are talking about those "garden inhabitants" who are 3 years old or more. The same people claim that shaping during the summer months allegedly leads to the active growth of new shoots.
Some believe that summer is the best time to process trees. But in our case, we are talking about those "garden inhabitants" who are 3 years old or more. The same people claim that shaping during the summer months allegedly leads to the active growth of new shoots.
How true this statement is, it is difficult to say. After all, there are many nuances in each case. As an experiment, you can try to prune a tree in the summer and see the result. And draw conclusions based on that.
At the same time, it was noticed that if pruning is carried out at the time of fruit filling, their quality increases markedly.
Another plus summer pruning lies in the juice secreted by the tree. It covers the wound, and this leads to rapid healing.
However, the vast majority experienced gardeners advises to prune when the tree is resting. Therefore, most often give their preference to early spring.
fruit tree age
 This operation can be started with one-year-old shoots to form the correct crown.
This operation can be started with one-year-old shoots to form the correct crown.
If the tree has reached 10-15 years of age, it is considered old. This assessment is connected with the fact that such trees have reduced yields and the number of growths. He needs a rejuvenating pruning.
It is performed on 3-7-year-old wood. But the next year, young shoots will thicken it. It is also necessary to ensure that the number of cuts on one side of the branch does not exceed 3.
What plants should be pruned
The pruning procedure should be carried out literally by all fruit trees in the garden. After all, it is she who leads to an increase in productivity, makes it possible to accelerate the growth of a tree, protects it from many pests and diseases.
When the leaves formed on the trees, it will be possible to prune only such plants as:
- Cherry;
- plum;
- apricot;
- cherries;
- cherry plum.
If this is done during the dormant period, then the procedure can provoke damage to trees by diseases and fungi.
Summer activities include:
- cut dead branches
- shorten young shoots
- remove branches that interfere with the crown.
Features of the procedure
 Pruning trees must be done very carefully and follow the basic rules so as not to harm the garden dweller.
Pruning trees must be done very carefully and follow the basic rules so as not to harm the garden dweller.
First of all, you should decide on the season suitable for pruning. It will depend on age and type. fruit plant, as well as the location of the garden and the local climate.
A large role as a result of this procedure will be played by the availability of tools that are necessary for its implementation.
To exclude an increase in the diameter of the damaged area on the bark, it is recommended to use only high-quality sharpened tools for cutting.
You need to stock up and have on hand such tools and items:
- ladder;
- secateurs;
- garden hacksaw;
- air pruner ( special tool on a long rod, designed to cut the upper branches);
- glasses;
- paint on drying oil or garden pitch - the means that are necessary to process the place where the cut will be.
It is contraindicated to perform excision with rusty instruments. Otherwise, the tree may die or become sick as a result.
Pruning scheme for fruit trees in autumn
Before proceeding with the pruning of fruit trees in the fall, the scheme of which is indicated below, it is necessary to determine why exactly it is needed and draw up a preliminary plan of action.
It's not worth it just to start shredding poor plants. In gardening, everything must be determined: both the type of plant, and the method of cutting it, and the goals pursued:

If there is a need to get the fastest growth from a fruit tree, then when pruning, you need to reduce the main number of fruit-bearing buds.
When the goal is determined, pruning patterns need to be studied. Several techniques are known, among which three are the most popular.

 If the cut diameter is more than 1 cm, then the wound must be treated without fail. To do this, they buy or prepare a special garden var themselves and treat them with wounds on the bark of trees.
If the cut diameter is more than 1 cm, then the wound must be treated without fail. To do this, they buy or prepare a special garden var themselves and treat them with wounds on the bark of trees.
If, for some reason, garden pitch does not fit well on the wound or does not fit at all, then you can use paint on drying oil.
The younger generation of fruit trees is recommended to be pruned solely in order to create the correct crown. Otherwise, this may lead to a decrease in their fruit-bearing properties.
Attention, only TODAY!
pruning garden trees no mistakes
To orchard pleased, he must be properly looked after. Proper shaping and reasonable pruning of a tree is an indispensable element of such care. But pruning is a kind of surgical operation that is painfully perceived by the plant, especially when it is illiterately performed. Unskillful intervention can lead to difficult-to-correct results, up to death.
Proper formation and reasonable, competent pruning of the fruit tree- indispensable elements of garden care. Many mistakes can be avoided by knowing the structure of the tree and the functional significance of its main organs and tissues, which act interconnectedly and do not replace each other.
Consider all this on typical apple or pear trees, simply calling them a tree.
Basics of biology
An ordinary varietal tree consists of a root system and an aerial part. Each of them has its own "duties". The roots are both the breadwinners and the foundation of the tree. They fix it in the soil, and most importantly, they provide water with minerals dissolved in it. As the tree grows root system also grows both in breadth and depth, going far beyond the landing pit (Fig. 1-1).
Rice. one
The place where the roots pass into the ground part is called the root neck (Fig. 1-2). In ordinary (not dwarf) trees, it cannot be buried during planting and subsequent care. Often the grafting site is taken as the root neck, but it can be at a height of 10-15 cm or more from it.
Varietal trees are obtained by grafting onto rootstocks, which are usually grown from seed. Seed offspring do not retain the characteristics of the variety, the trees grown from them are most often wild, with fruits unsuitable for use. Therefore, the rootstock is usually called a wild, and the grafted variety is a scion.
The grafting site is usually well visible in seedlings and young trees. It, as a rule, is distinguished by a noticeable curvature and scars or a slight influx at the junction of the rootstock with the scion. All shoots growing below the grafting site are not varietal, they are called wild shoots. Such shoots must be removed in a timely manner, as it develops to the detriment of the tree.
The ground part of the tree consists of a trunk (Fig. 1-4), usually growing vertically, from which lateral branches form a crown. The trunk is the central part of the tree from the root neck to the very top. It is a support for the crown, and its internal tissues serve as a "overpass" for the movement of water and various nutrients.
The lower part of the trunk from the root collar to the first skeletal branch is called a trunk (Fig. 1-3). Its height can be different, usually not lower than 50 cm (for ease of care) and not higher than 1 m (for an acceptable tree height). The trunk above the stem and to the very top is called the central conductor, or leader. It ends with a one-year continuation shoot (Fig. 1-7).
The branches extending from the trunk form, as it were, the backbone of the crown, which is why they are called skeletal (Fig. 1-5). They host branches of the second, third and subsequent branches, which end in overgrown branches with annual growths (shoots) (Fig. 1-6). The boundaries of increments are visible on the outer annual rings in the form of narrow scars of the bark. From them you can determine the age of the branches. Each growth ends with an apical bud, and vegetative (growth) buds form in the axils of the leaves. In the spring, leaves and new shoots sprout from them. In early-growing varieties, flower buds are also formed on annual growths, which are distinguished by larger sizes.
In most varieties, the crop is formed on the fruit formations of overgrown branches. The shortest of them (1-5 cm) are kolchatka, which then grow into branched fruits. Their productive age is about 10 years. Longer fruit formations (5-15 cm) are called spears, and the longest ones (from 15 cm) are called fruit twigs. They end in flower buds that give both fruits and rosettes of leaves or new shoots. Most varieties have mixed type fruiting.
Varieties with annular type of fruiting are most preferred. As a rule, they are early-growing, fruitful, with a compact, non-thickening crown. But due to congestion with flowering and harvest, varieties with annular type of fruiting have attenuation of growth and a deficiency of leaves, which leads to crushing of fruits, their shattering, and a decrease in winter hardiness. In such cases, special pruning is necessary to stimulate the growth of shoots.
It is the shoots that are the main base of the leaves, and they are the same breadwinners of the tree, like the roots, only they provide different food products. From the soil along the wood of the trunk and branches, water with minerals dissolved in it enters the leaves. And they, in the process of photosynthesis, form organic substances (assimilates) necessary for the growth and development of the whole tree (including the roots), the creation of a crop and a safe overwintering. Assimilates come to all organs of the tree by a downward current through the vessels of the bark of the branches and trunk.
Between the bark and wood is a special "building" tissue - the cambium. It is invisible to the eye, but during the period of sap flow, in late spring and summer, it is a gentle slippery layer under the bark. From spring to autumn, the cambium actively works, laying bark cells outside, and wood inside, due to which the trunk and branches thicken. Thanks to the cambium, vaccinations grow together, wounds heal: on the wounded surface, its cells quickly divide and form an influx of callus, and from it - bark and other tissues with vessels.
Any annular damage to the bark along with the cambium on a branch or trunk leads to their death, as it interrupts nutrition. Therefore, any harnesses, ropes, etc., that cause constrictions, should not be allowed to cut into the bark.
The purpose and objectives of pruning
Pruning is the partial or complete removal of some branches in accordance with the tasks for which plantings are grown. For example, ornamental trees and shrubs are trimmed to create a variety of shapes and configurations. Mother-cutting plants are specially pruned very heavily in order to mass regrowth of young shoots necessary for reproduction in nursery farms. Such techniques are completely unsuitable for consumer gardens.
The main goal of pruning a fruit tree is to form a correct, strong crown at a young age and correct it during the fruiting period in order to obtain high-quality crops as quickly as possible and for a long period.
Specific pruning tasks may vary due to age-related changes in plants. At a young age (conditionally up to 8-10 years), pruning should be minimal and only auxiliary to form the correct crown. During this period it is important:
Ensure optimal development of the central conductor for the timely growth of a strong crown on it.
Arrange the branches evenly on the trunk so that each of them is in favorable conditions solar lighting and aeration (i.e. free access of air).
During full fruiting, in addition to those mentioned, new tasks appear:
Regulate optimal growth and fruiting.
Protect the crown from thickening and growth in height.
Extend the productive period of the tree.
During the aging period of a tree (if it is winter-hardy and not damaged in any way), the crown can be updated with rejuvenating pruning.
Pruning timing
Tree pruning is one of the earliest jobs in the garden. The best time for this is the beginning of spring, when there is no danger of frost and the buds have not yet begun to bloom. In winter, pruning is carried out only in those southern regions where the risk of frost damage is low. In the central part of Russia, winter pruning is dangerous due to the unpredictability of the onset of frost, during which not only the exposed tissues of the cuts are damaged, but also the bark and cambium near them. Sometimes, even in the so-called mild winters, after prolonged thaws in late February - early March, there are frosts down to -20-25 °. In such cases, it is especially dangerous to inflict large wounds when cutting skeletal branches in the lower part of the trunk, close to the snow surface, where the temperature is always lower, and it can be critical for the cut surface.
Specific calendar dates for the optimal period spring pruning may change depending on weather conditions. In the Moscow region, they usually come from mid-March, when the snow has not completely melted and the feet do not get stuck in the slushy ground. But main criterion timely pruning - have time to carry it out before the start of sap flow. What it is? When the average daily air temperature is above 5 °, the vegetation of plants begins. It is accompanied by active spring sap flow, i.e. the roots supply water with minerals dissolved in it up the vessels of the wood to all organs and tissues of the ground part. It is easy to verify the intensity of sap flow from the well-known fact of the release of birch sap.
With timely pruning before the start of sap flow, the surface of the cuts is dry, and garden pitch easily sticks to it, which is necessary to protect exposed tissues from drying out, freezing and ingress of pathogens for the entire period until the wound heals. In addition, the vessels cut at this time are immediately filled with air, which, like a cork, clogs them and prevents the juice from flowing out during subsequent sap flow. And with belated pruning during sap flow, all vessels are already filled with moisture. The var by itself does not adhere well to a wet surface, and even is rejected, as it were, by the juice gushing from the wound. Such "weeping" trees are depleted in vain. In addition, the juice flowing down the bark becomes a breeding ground for harmful pathogens, and in particular, sooty fungi. Their black dense coating clogs the stomata (small holes) of the bark, while disrupting the necessary air exchange and reducing winter hardiness. Therefore, for trimming and set the optimal time.
But if the winter was frosty, pruning should be delayed until obvious damage appears. Only obviously dead parts of the crown should be removed immediately.
Regardless of the season, only the so-called sanitary pruning is carried out - forced, unplanned removal of broken, sick, drying, etc. branches or parts thereof. Sanitary pruning is performed as soon as dangerous defects are identified to prevent further deterioration of the tree. For example, from strong winds, adhering wet snow, branches with a tear of the bark on the trunk often break. If such a "hanging on a string" branch is not cut off in a timely manner, damage to the bark will increase.
If there is a need for pruning in the winter, then it should be done during the thaw period. In frosty weather, the wood is brittle, it is chipped from the cutting tool, damaging the underlying tissues. When cutting a thick branch, you must first leave a stump 15-20 cm long so that it takes the frosty blow on itself, and not the exposed surface of a large wound. And in the spring this stump must be removed according to all the rules of pruning - on the ring.
What you need to trim
The main pruning tools are a pruner (for thin branches) and a garden (but not carpentry) saw for thick branches. All tools must be in good condition and sharply sharpened. Not only the ease of doing the work depends on this, but also the correctness of the cuts with better healing of wounds. Therefore, you will also need a whetstone (whetstone), a whetstone and a file for sharpening the saw. Garden secateurs should have blades tapered at the ends, widely diverging in the working position. Secateurs with wide ends of the blades are difficult to bring closer to the cut lines, difficult-to-overgrow stumps remain. The secateurs must be adjusted in such a way that no gap is formed between the cutting blade and the counter-cutting plate during operation, leading to jamming and crumpled wounds on the branches. A good pruner should cut correctly with the entire surface of the blade, especially the tip.
For more accurate and accurate cuts of thick branches, it is better to use a special garden file, and not a pruning shear (with long handles), often leaving hemp. A good garden saw should have a quality cutting blade with a tapered end and a strong attachment to the handle (at its base there should be no gaps when checking by moving left and right). The correct saw has widely spaced (a little more than twice the thickness of the blade) and sharply sharpened teeth, which make it easy to make forward and reverse motion.
In some cases, a sharply sharpened garden knife (sickle-curved) is also needed to smooth out uneven cuts, cut the bark during certain operations, etc.
All cuts or other wounds with a diameter of more than 1.5-2 cm require surface protection of exposed tissues from drying out and ingress of harmful pathogens. For this, various garden putties are used, the best option of which is garden pitch. A good pitch is always soft (even in the cold), easy to apply without preheating, and sticks to the cuts normally. Var should carefully cover all surfaces of wounds, but do not apply too much, a thin layer of its fatty base is enough. Excess var is harmful, because, melted in the sun, it will flow down the bark, clogging its microscopic holes (stomata) and making it difficult for the necessary air exchange. Do not forget that all work in the garden must be carried out meaningfully, without violating the natural physiology of plants.
Slicing technique
Before proceeding with pruning, it is necessary to master the technique of performing its techniques. Take your time to approach the fruit tree with cutting tools, practice first at least on wild trees.
When pruning, two main techniques are used: removing the entire branch and shortening it. In both cases, you need to learn how to make cuts correctly. Annual growths and thin, up to 2-3 cm thick, branches are usually pruned or removed with secateurs. The pruner should be held in such a way that four fingers are on the handle of the cutting (wide) blade. In this case, the handle of the shear plate should rest on the palm under the thumb (Fig. 2). If this tool is not positioned correctly in the hand, when the fingers grab the handle of the anti-cutting (narrow plate), firstly, additional efforts are required, and secondly, this leads to crumpled wounds on the tree and rejection of the bark.
Rice. 2. Cutting branches with secateurs: A- correct; B- correct cut with secateurs; IN- incorrect position of the secateurs (cannot be installed from top to bottom)
To remove a branch, bring the secateurs from below, placing its lower blade on the surface of the annular influx. Lightly pulling the branch with your hand makes it easier to cut, and it turns out even.
Remember important rule- any cut should be made not anywhere, but only over a well-developed bud or branch directed in the direction necessary for the crown. In such cases, they usually say: pruning on a kidney or transfer to a branch.
To expand a crown that is too compressed, cut to the outer bud (or branch), that is, make a cut above the bud that is located on the outside of the branch. A drooping crown can, on the contrary, be raised by cutting it to an inner bud or branch (Fig. 3).
Rice. Fig. 3. Results of pruning a tree for the outer (A) and inner (B) buds. The black color shows the previous direction of growth.
It is important to correctly make the cut itself over the kidney (Fig. 4). It should be slightly inclined to drain the water that falls on it, but with a minimum surface. The upper part of the cut should be at the level of the apex of the kidney or 2-3 mm higher. You can not leave a higher stump above the kidney, as it will interfere with overgrowth. It is also impossible to make an oblique cut that is too low - its large surface will cause the kidney located opposite such a cut to dry out. The same principle is preserved when shortening branches, when by transferring to various branches, growth can be directed to the right place in the crown. If it becomes necessary to remove the entire branch, then cut it “into a ring”. What does it mean? Look at the base of a branch at an angle greater than 30° and you will see an annular fold (Fig. 5).
Rice. 4. Pruning on the kidney: A- correct; B- incorrect (too high, the stump will interfere with the healing of the wound); IN- incorrect (cut too low and large)
In young trees with elastic bark, the influx is slightly wrinkled, folded. It is there, under the bark of the influx, that special tissues are concentrated, due to which the wound heals. Therefore, the cut must be made, focusing on the top of the influx (Fig. 5 A), without leaving a hemp and at the same time without touching the trunk, that is, without going deep beyond the influx. Since in this case the cut surface increases (and it should always be reasonably minimal), but the main thing is that such a valuable “ring” is cut off and a wound that is difficult to heal is formed (Fig. 5 B).
Rice. 5. Cut for the ring: A - correct (along the top of the annular influx); B - incorrect (stump left); B - incorrect (too large, the annular influx is cut out)
A common mistake is leaving a stump when removing a branch (Fig. 5 B). Too long a stump, left, as a rule, “out of pity”, overgrown with new shoots in the first year. As a result, instead of one branch cut for thinning or lowering the crown, many new ones are formed.
A short stump, as a rule, does not give new shoots, most often it dries up. But when drying, the bark gradually, as it were, “slides down”, exposing the wood. If the error is not eliminated in time by cutting off the stump as expected, the “slipping” of the bark and drying out of the wood can destroy the trunk with tissue necrosis, a hollow, the introduction of diseases and pests, so even if it becomes necessary to temporarily leave a stump (thorn) to tie an escape to it, do not forget to delete it later.
If you need to cut a branch growing at an acute angle, around which the influx is invisible, use a simple trick to determine the correct cut line (Fig. 6) - draw a line with chalk (or mentally) along the trunk or branch from which the cut branch (AB) departs, and the second - perpendicular to the cut branch (AG). Divide the angle between them in half and guide the cut along this line (AB).
When cutting branches, first file them from the bottom, otherwise the bark will be scuffed, after which the wound is difficult to heal (Fig. 7A). It is better to remove large, heavy branches in parts: first, as deeply as possible (until the file jams), file the branch from below at a distance of 30-40 cm from its base. Then, retreating another 10-15 cm from the base, saw the branch from above. Under its own weight, it will break off, but the peeling of the bark will not occur due to the lower notch. After that, the remaining stump is not difficult to remove according to all the rules on the ring (Fig. 7 B).
Rice. 6 Definition right direction cutting off a branch at an acute angle
All cuts and saw cuts should be even and flat, do not make any roundings on them. And do not forget to immediately cover them with garden pitch.
Near large wounds, the growth of new top shoots usually begins. If they are not needed to replace branches or otherwise correct the crown, they must be broken out in a timely manner, preventing them from growing, otherwise they will have to be cut again later.
Rice. 7. Sawing large branches: A- not right; B- right; one- the first filed from below; 2- the second filed from above; 3- hemp tenderloin
When pruning, it is impossible to inflict many wounds on the trunk in one year, especially close ones. This violates the integrity of the cortex, through the vessels of which there is a downward outflow of photosynthesis products to the roots. As a result, their starvation begins and, as a reaction to this, the appearance of wild growth, which will weaken the tree.
"Self-destruction" of unnecessary branches
It happens that shoots begin to grow in places that are hard to reach for cutting, for example, between the trunk and the skeletal branch. They must be broken out in a timely manner, while they have not yet had time to lignify. But usually they are not noticed at first, but pay attention when they already become strong branches and threaten dangerous sharp corners. Neither a file nor a pruner can get close to the place of the required cut: either the wound will be too large, or a drying stump will remain, and this will cause damage to the bark under it. What to do?
In such cases, I use my own technique of “self-destruction” of an unnecessary branch according to the principle of constriction. To do this, it must be tightly pulled with a wire in the place where the cut should be. Such a specially arranged ring will gradually cut into a thickening branch, and then it will easily break off in the right place. The wire must be flexible for tight wrapping around the circle and not thin (at least 3-4 mm), otherwise the edges of the cut bark will simply close and growth will continue. To prevent the wire from slipping, it can be fixed with an incision on the bark in any convenient place.
No sharp corners
For a fruit tree, the strength of the crown is especially important, capable of withstanding the weight of large crops in summer and adhering snow in winter, strong gusts of squally winds, etc. Strength depends on winter hardiness: damaged wood of trunks and branches gradually becomes rotten and therefore easily vulnerable. But why do branches often break off even in the most winter-hardy varieties without the slightest sign of freezing, as evidenced by light dense fabrics on break? Typically, such breaks occur in trees with sharp angles of branching from the trunk.
Many do not pay attention to the plant from a young age, letting its development take its course. This leads to various crown defects, the most dangerous of which is a bifurcation of the trunk or skeletal branches closely pressed against it. In such cases, sharp corners are formed between them, dangerous for the structure of the tree. Their harmfulness manifests itself gradually and consists in the following.
Branches extending from the trunk at an acute angle have an unstable accretion at the junction and break off over time. Figures 8 and 9 clearly show the reasons for the breakage of a branch due to an acute angle of departure. In the first case, the branch departs from the trunk at an angle close to a straight line (Fig. 8). The numbers indicate the sequential formation of wood in each year of growth. The growth of annual layers occurs due to the activity of the cambium (indicated by the letter C), located between the bark and wood. Let me remind you that the cambium is a special, very thin, but extremely important plant tissue. By dividing its cells, new layers of wood and bark are deposited, so the branches thicken.
Rice. 8. Fig. nine.
With a large angle of branching from the trunk, the wood tissues grow together without hindrance, and the connection at the points of their connection is strong. Such branches can bend to the very ground, but do not break off the trunk.
In another case (Fig. 9), annual layers of wood are visible on each branch, but they cannot grow together with each other. This is prevented by the lower sections of the bark (Ko), which gradually, with the thickening of the branches, are sandwiched between them. As it grows, the thickness of the bark clamped inside increases and becomes, as it were, a spacer between the branches. In addition, moisture accumulates in the fork and harmful microorganisms settle. As a result, without vulnerable spot rots inside (HA), which further reduces the strength of fastening branches. Therefore, do not allow the formation of sharp corners in the crown, form a tree from a young age, correct any violations in a timely manner.
Particularly dangerous can be a bifurcation of the trunk at the top, which must be corrected immediately after the appearance by removing one of the parts (Fig. 10). If time is lost, then as the tree matures, a tear will begin between the oppositely located trunks. At first, it is noticeable by the crack that has formed, which can subsequently lead to the splitting of the trunk to the very ground. Fastening the emerging tear with metal staples or various harnesses, as is usually recommended in such cases, will save for a while.
Rice. 10.
To prevent this, it is necessary to choose a better developed part of the trunk, and first greatly shorten the other. After two years, the dominant part, left without pruning, will become much thicker than the previously shortened one, and then the former competitor can be cut down to the base on the ring. In this case, the wound will heal faster, because. it will be less than the diameter of the trunk.
branch bending
An unformed five-year-old tree that formed a bifurcation of the trunk: 1- a branch cut to the base; 2- branch left to form the correct crown
To avoid sharp corners, bending branches in young plants will help, while they are thin and flexible. To do this, use the tying of branches to the trunk or to stakes driven into the ground, pulling with spacers or weights (Fig. 11). Bending should be carried out before the lignification of the shoots, which begins in July. Then the bent branches retain the angle of departure from the trunk given by them. This technique also accelerates fruiting, limits the size of the tree, and provides good illumination inside the crown. As a result, the harvest is more plentiful and of better quality.
Rice. eleven.
In many countries with developed fruit growing, branch bending techniques are used in very young trees. In Poland, for example, such formation is carried out at a very early age, when lateral branches are just beginning to grow in an annual plant and are only 15-30 cm long. And they use ordinary clothespins for this (only wooden ones). The clothespin is fixed on the stem in such a way that by bifurcation it rests against the base of the shoot, deflecting it to a horizontal position, that is, the clothespin serves as a spacer between the trunk and the shoot. This work must be carried out in a timely manner, around the middle of summer (depending on weather conditions and the degree of development of plants). It is important to have time to act on young shoots before they are lignified, when they are still flexible and easy to bend, so as not to injure or break.
Clothespins are also used to attach small cement weights with a short loop to already lignified shoots (so as not to injure the plants when swinging the weight). Of course, the size of the weight must be commensurate with the shoot so that it does not break off.
You can simplify all this by putting, for example, small pebbles in rag knots and securing them in such a way that the side shoots take a horizontal position.
However, the effect will be achieved only if the branches are given a strictly horizontal direction, and not bent at random. If, for example, they take an arcuate position, then strong vertically growing shoots will appear at the highest point of the arc - tops, which will only thicken the crown. Therefore, branches should not be nailed or tied to the trunk by the ends - in this case, arcs unnecessary to the tree are formed. It is necessary to pull the branch by tying the twine in its middle or closer to the base.
Branches with a thickness of 2-3 cm in diameter are already difficult to bend, they break off with scuffs of the bark on the trunks. It is possible to increase their angle of departure from the trunk only with preliminary sawing (Fig. 12). The cuts are made from the bottom near the very base of the branch by about 1/4 of its diameter. With a thin, sharp file from the bottom of the branch near its base, make 6-8 cuts at a distance of about 2 cm from one another. After the branch is bent, it must be secured with two stretch marks to the pegs. Wounds from filing when tilted are clamped and quickly overgrown.
Rice. 12.
To understand the essence of this technique and feel its benefits, practice first on some other tree with branch flexibility similar to an apple tree.
All these rules and techniques will help the correct formation and pruning of the tree.
We form new plants
There are various systems for shaping trees, but for amateur gardening, the main type is a free-growing tree, rounded, with some size limitation later on. The crown must have the correct ratio of skeletal branches and the central conductor ( top part trunk). It should dominate the branches in height and thickness. After reaching the desired height of the tree, the conductor is shortened.
In an adult tree, skeletal branches should be evenly distributed along the trunk from all sides at a distance of no closer than 30-40 cm one above the other for their normal illumination and general development. Branches should not overlap, intertwine, etc.
Formation must begin with new plants - this is how young trees are called during the first two to three years after planting. Already in the spring, they may have unequal development associated with different survival rates, freezing, drying, etc., therefore, the approach to each plant should be individual.
An ideal option for a one-year-old is when all the buds bloom, including the apical one (Fig. 13), and already at the end of June there are growths of 20-30 cm. In such a one-year-old, you just need to cut a spine - a stump left from the wild game when tied in it shoot (the cut is shown in the figure by a solid line).
Often in one-year-olds, unripened tops freeze slightly (Fig. 14). Cut off the frozen part in the spring on a strong bud, leaving about 10-12 cm as a spine for tying the shoot to it, which will appear from the upper living bud (dotted line). Remove the spike afterwards.
If frozen ground part to the level of snow, the plant can be restored the same way(Fig. 15).
But if such freezing is repeated annually, this is a sign of the non-winter resistance of the variety, its unsuitability for the area.
Rice. 13. Fig. 14. Fig. 15.
Some trees may bloom in the first season after planting. This is characteristic of early-growing varieties, in which flower buds are laid on annual growths. Due to the fact that flowers young plant consume the supply of food that is required for the development of the tree, the buds must be cut off before they bloom. And next year, the flowers can already be left, if, of course, the tree grows and forms normally.
Now consider the most typical faults crowns biennial plants, shown schematically in the figures. The dashes indicate the places of the necessary cuts. You should pay attention to the different angles of inclination of the lines, which indicate the correct inclination of the cut above the kidneys.
On fig. 16 the central shoot ends with poorly formed buds, becomes very thin towards the top. It must be shortened by cutting over a strong, well-developed kidney. For the same reason, branches 1, 3, 4 and 5 are cut in the same way. At the same time, the 3rd, 4th and 5th branches are cut to the outer bud to expand the crown, and the drooping 1st to the inner bud to raise it. Branch 2 is not cut, as it ends in a well-developed apical bud.
Rice. 16. Fig. 17.
On fig. 17, the upper lateral shoot (5) is not inferior in strength to the central conductor (6), it has become its competitor, and it leaves at an acute angle, which will inevitably lead to a trunk break. Therefore, the competitor must be removed or severely cut off on the outer kidney. Shoots 3 and 4 are cut to a strong outer bud at approximately the same crown level, taking into account the subordination of branches, and shoots 1 and 2 are not cut, as they end in well-developed apical buds.
On fig. 18 the central conductor is too strong, grows to the detriment of the lower side branches. Therefore, we shorten it by almost half. The lower shoots are slightly pruned to a strong bud only if their apical buds are less developed than the lower ones.
On fig. 19, the central conductor was shorter than the lower side shoots. There are two ways to correct the crown. If the central conductor is strong enough (normal thickness, well developed buds), but the top has been broken, it can be left, shortening the lower shoots accordingly to coordinate the branches in the crown. If the shoot located below - the competitor (3) is more developed, then it is transferred to a vertical position (shown by the dotted line), attached with garters to the central conductor (5), which is subsequently cut out. So that the shoot (4) does not turn out to be a competitor, it can be removed, but, given the bareness of the crown, it is left, greatly shortened to the outer kidney. The rest of the shoots are shortened if necessary.
Rice. 18. Fig. 19.
On fig. 20 shows the case where the center conductor is missing. Here, a strong lower shoot (6) must be transferred to a vertical position. But since there is nothing to tie it to, a rail is attached to the upper part of the trunk, to the end of which a shoot is tied with a “eight”.
Pruning of the remaining shoots is carried out according to the same rules as in the previous examples. All branches left in the crown, extending from the trunk at an acute angle, must be bent in a timely manner to a horizontal position, while achieving an increase in the angle of departure.
Rice. twenty.
Rice. 21. Varietal characteristics of biennial branches of an apple tree: A- bud awakening and branching are good (Melba); B- the awakening of the kidneys is good, the shoot productivity is weak (Grushovka Moskovskaya); IN- bud awakening is poor, branching is weak (Cinnamon striped)
In the subsequent formation and pruning, one should take into account the awakening of the buds and the shoot-forming ability, which depend on the varietal characteristics and age period trees (Fig. 21). In apple tree varieties with poor bud awakening and weak branching (Cinnamon striped, Mayak, Medunitsa, etc.), without pruning, the branches are ankle-shaped (bare), the crown is fragile, consisting of forks, and fruiting quickly moves to the periphery. In varieties of this type, to enhance branching and the formation of fruit twigs, it is necessary to apply transfer to lateral branches on two-year-old wood (Fig. 22).
Rice. 22.
Trees of cultivars with good bud awakening but poor shoot productivity (Grushovka Moskva, Borovinka, Bessemyanka Michurina, etc.) usually form their crown well and do not need strong thinning. They only need to remove “competitors” if necessary, subordinate the main branches to the central conductor and slightly shorten strong annual growths.
Trees with good bud awakening and medium branching (Antonovka vulgaris, Papirovka, Welsey, etc.) require moderate pruning during the formation period. Their skeletal branches are subordinated to the central conductor, pruning is carried out on the side branch.
Varieties with good bud awakening and good branching (Streifling, Melba, Zvezdochka, Severny Sinap, etc.) are prone to thickening. They should not shorten strong branches at a young age, as this will increase thickening, but it is necessary to constantly thin out the crown in the future.
fruit garlands- good or bad
The abundant flowering of trees, and then the garlands of fruits on them, usually pleases everyone. Indeed, this is evidence of their good overwintering, as well as a high level of adaptation to the bad weather of past years. This means that the varieties are correctly selected, they are both winter-hardy and productive.
And now we need to look from a different perspective: if all the branches are covered with flowers to the very tips, then there are no young growths with breadwinner leaves at all. The crop in this case is forced to develop only at the expense of those few leaves that are next to the fruits. But this is too little, especially for varieties that bear fruit in “garlands” (cover photo). Special studies have established that for the normal growth and development of one fruit of an apple or pear tree, at least 30 leaves are required. They are also necessary for the general development of the tree: feeding the roots, laying the future crop, preparing all organs and tissues for overwintering, etc. Therefore, the lack of leaves creates problems for both the tree (decrease in potential winter hardiness and productivity, general depression, weakening resistance to pests and diseases) and the gardener (too small fruits, their premature shedding, poor storage, etc.).
What is the conclusion from all this? It is impossible to run a tree to such a state when it does not have increments. This is usually observed in trees of venerable age, which require crown rejuvenation. But the attenuation of growth can also occur in not yet old trees with a predominance of the annular type of fruiting. This is most characteristic of many pear varieties (Lada, Chizhovskaya, Petrovskaya, Yuryevskaya, etc.). Yearly, from an early age, crops deplete them, and in addition to proper, balanced nutrition, they require periodic corrective pruning to stimulate shoot growth.
Optimum for a fruit-bearing tree, shoots are considered to be at least 50-60 cm long in the upper part of the crown (here they are always stronger), 30-40 cm in the middle part and 20 cm in the lower part. Reducing these sizes is a signal for timely pruning, which will help restore the necessary balance between the generative (fruit-forming) and vegetative (growth) parts of the tree.
Rice. 23.
In a neglected tree, such pruning is carried out according to the principle of lowering, thinning and general rejuvenation of the crown. It is schematically shown in Fig. 23 before and after cropping. Please note that when the crown is lowered, oppositely located branches should not be left on top - a break will occur from the severity of the crop. In the picture shown, the cropping is done correctly.
Without tops
If you form it correctly and cut it off in a timely manner, then you won’t have to remove too much, and this will only benefit the tree. No wonder one authoritative scientist wrote: "Large heaps of cut branches under fruit trees ... serve as an accusation against the owner of the garden and indicate that in previous years he did not fulfill his duties." And indeed, after all, pruning for a tree is the destruction of the work already done by it, the waste of accumulated nutrients. But the main thing is that strong pruning stimulates the growth of many new shoots, which are called tops.
Spinning tops are powerful "fat" (that's why they were called "wen"), shoots growing intensively upwards. They appear for various reasons: after mechanical damage to the trunk or crown of a tree, with improper (arc-shaped) bending of branches, unbalanced nutrition (with excess manure, nitrogen fertilizers), in aging trees, etc. But most often, the formation of tops is a natural reaction to a strong pruning of the roots, seeking to restore their relationship with the previous volume of the crown.
Surely, many have come across such a phenomenon when, after a strong reducing and rejuvenating pruning of an old tree, in the very first season, a whole forest of tops grows up to 1.5-2 m high and is much larger in thickness than ordinary growths. And the next year they had already branched out and increased the unnecessary 2nd and 3rd "floors" of the tree instead of the necessary reduction in the crown. Not only is the tree now taller than before, but these young floors are also developing to the detriment of the fruiting and development of the crown, shading it, taking away valuable nutrients (hence the name - spinning tops) and weakening in general.
Therefore, a thorough pruning to reduce or rejuvenate the crown is best done not immediately, but gradually over 2-3 years, then there will be less gyration. In the first year, it is necessary to open the center of the crown, shortening the central conductor from above by transferring to a strong side branch (Fig. 24). In the second year, cut large thickening branches from the middle of the crown. After that, shorten the remaining branches to the first or second tier of branching by transferring them to branches oriented to the periphery of the crown, and remove the lowest drooping branches. Naturally, all diseased, dried, rubbing against each other branches should also be cut out.
Rice. 24. Scheme of pruning an adult tree with a narrowed crown. Branches to be removed are shown in black: A- crown periphery; B- central conductor; IN- large thickening branches; G- lower drooping branches
Unnecessary tops should be broken out immediately after the start of their growth, preventing subsequent lignification. In the middle - late summer, it is already too late to remove them in this way, and cutting them into a ring with pruners is risky, as there will be too many wounds that will not have time to heal before autumn. But you can cut it off, leaving 5-10 cm stumps, and in the spring, do not forget to remove them in accordance with all the rules. Please note that young shoots may appear on such stumps even at the beginning of autumn, they must be broken out without fear.
No wild growth
One of the indispensable elements of spring pruning is the removal of wild growth, i.e. shoots growing below the grafting site. They become a competitor for water, food and therefore deplete the tree.
Usually the branches of the savage differ markedly from the cultivar in leaves, buds, bark color and other features. But often this is not noticed, and as a result, both a cultivar and a savage grow on the same tree. And only when its branches begin to bear fruit, bewilderment arises: why have the apples become completely different, has the variety been reborn?
To prevent this from happening, the shoots of wild shoots must be broken out at the very base, as soon as they begin to grow. Unfortunately, they are often paid attention to when they are already lignified and cutting with a pruner is required, and in an advanced case, with a saw. If this work is carried out at the same time as pruning in early spring, when the snow around the tree has not yet melted, stumps usually remain. Soon they are overgrown with many new young shoots, turning into whole bushes around the tree. To prevent this, as soon as the snow melts, the stumps must be cut to the ground. If necessary, you will have to dig up the ground to get to the place where the overgrowth grows. Cover the cuts with pitch and cover with soil again.
However, it is important not only to correctly remove wild shoots, but to identify, eliminate and prevent the causes of their appearance in the future. They can be different, most often the following.
The result of a strong pruning of many branches at once. Shoots appear in response to an imbalance between the roots, programmed for the previous volume of leaves in the crown, and a sharp decrease in the nutrition coming from them.
Strappings, labels, etc. not removed in a timely manner. cut into branches thickening in the process of growth. This interrupts the downward outflow of plastic substances, which occurs through the outer tissues from the leaves to the roots. The roots, deprived of the necessary nutrition, are forced to help themselves with the formation of overgrowth. Therefore, do not tie anything close to the trunk or branches.
The consequence of starvation of the roots due to the physiological incompatibility of the stock with the scion, when the exchange of nutrients between them is disturbed. This phenomenon is usually accompanied by a noticeable thickening over the grafting site, too early entry into fruiting and at the same time weak or absent growth, premature autumn coloring and leaf fall, and a decrease in winter hardiness. Such trees are gradually dying.
A signal of winter and other damage that was not noticed in time: frost cracks, sunburn and cracking of the bark, damage to it by cytosporosis, black cancer and other diseases. With severe damage, the ground part gradually dies, and healthy roots that require plastic substances give rise. In the last two situations, drying trees must be cut down to the ground, and strong growth can be used to graft a more winter-hardy variety.
N. Efimova , candidate of agricultural sciences
(Garden and garden, newspaper library No. 3, 2008)
Pruning fruit trees in the garden in the photo
Before properly pruning fruit trees, we carefully look at the annual growth and select a bud that looks in the desired direction. Where the kidney is directed - there in the next season the shoot will grow, which will develop from it, in the future it can become a large branch. We hold the secateurs slightly obliquely, so that the lower edge of the cut is at the level of the base of the kidney, and the upper one is at the level of its tip. (If you hold the pruner in a different way, then it can be argued that the kidney will be seriously damaged.) The cutting blade is on the side of the remaining kidney, and the support blade is on the side of the removed part of the branch. The cross section is not a circle, but an ellipse. The cut when pruning fruit trees is done in one decisive movement.
The first common mistake is that the cut is too high and the stump is too big. It will still dry out at least to the nearest kidney, and if pathogens get into the wound, the process can rapidly go further.
Proper bud pruning of fruit trees is a delicate job. Therefore, the quality of the tool and the sharpening of its blades are of particular importance. It directly depends on how quickly the cut will grow.
The second common mistake is cutting too low. The kidney is damaged, or at least the vascular bundles that branch off the stem and go to the kidney. Transport flows are disturbed, with a high probability the kidney will die, and after it - the area of the escape located below.
These photos show how to properly prune fruit trees for a bud:


Proper pruning of fruit trees on a ring (with video)
 Pruning fruit trees on a ring in the photo
Pruning fruit trees on a ring in the photo  With further growth and development, the boundaries of increments are erased, but with a little practice you will learn to see the annular influxes (photo)
With further growth and development, the boundaries of increments are erased, but with a little practice you will learn to see the annular influxes (photo)
To prune fruit trees as carefully as possible, you need to clearly understand where the rings are on the branch. At the base of the growth of each year (the kidney ring is formed by scars of fallen kidney scales). On young branches, bud rings are clearly visible; growths of the current year usually have a brighter and shiny bark. With further growth and development, the boundaries of increments are erased, but with a little practice you will learn to see ring-shaped influxes (“bark folds”). It is in the annular influx that the wound meristem arises. Wood and bark form from the wound meristem and close the wound at a rate of about 1 cm per year.
If the branch is thin - take a pruner. We have it with a working blade towards us. We hold the branch to be removed with the other hand and slightly move it away from us - with tension, the cut is easier to perform. Rezhem. The manufacturer has already made sure that the pruner blades are correctly adjusted, and the cut goes where it is needed - it will protrude slightly to the touch. It is right. When pruning fruit trees in the garden, don't aim for a "flush" cut, as you would with carpentry and construction work. Beautiful - yes, perhaps, but it will take longer to overgrow the cut, and the big question is whether it will overgrow - you have removed the annular influx “with meat”. We don’t leave stumps either; if necessary, we trim the cut with a garden knife.
If the thickness of the branch is such that you doubt that you can handle it by working with a pruner, we take a hacksaw (I repeat especially for the stronger sex - a hacksaw, not a chainsaw). The branches have a habit of breaking off suddenly, leaving long-healing bark marks. To prevent this from happening, we always start working with a hacksaw from the bottom up. We find an annular influx, try on and start sawing. Sawing as much as it turns out, holding the branch to be deleted free hand and slightly take it away from us and slightly up so that the hacksaw blade is not clamped in the cut (you will certainly feel if this happens).
Then we move on to the second action - we begin to cut from top to bottom - again along the annular influx. We hold the branch to be sawn off with our free hand. Ideally, the cuts converge to form a single, smooth cut. In practice, this does not always work out, therefore, if necessary, we level the cut surface with a garden knife. Be sure to cover the cut with garden pitch or similar compounds.
Watch the video of pruning fruit trees on the ring:
How to properly prune a fruit tree if the branches are at an acute angle (with photo)
And how to properly cut the branches of fruit trees if they grow at an acute angle? Usually, in a situation where the branch departs at an acute angle, the annular influx is poorly expressed. You will have to remember school geometry lessons to find the cut line (you can use chalk, charcoal, a marker or a bar of soap and make a drawing right on the bark). In many cases, this is also the most convenient line to work with.
- We outline a line parallel to the branch that remains.
- We outline a line perpendicular to the branch to be removed.
- Find the bisector of the resulting angle. This is the optimal cutting line.
- We carry out the cut, starting to work with a hacksaw from the bottom.
- We complete the cut with a saw cut from above, trim if necessary and be sure to cover it.
Sharp corners in the crown are very dangerous - these are potential places for unexpected and serious faults. Faults can appear at any moment, they overgrow for a long time and painfully. Risk factors are a high harvest, heavy rain and wind or even snow, which often accumulates in forks.
Of course, it is necessary to correct such a serious defect as an acute angle as soon as possible.
Often, in mature trees, it is no longer possible to eliminate this deficiency without inflicting large wounds. In this case, the decision is often made to leave the branch - on the principle of choosing the lesser of two evils.
These photos demonstrate how to prune fruit trees if the branches go at an acute angle:


How to properly prune fruit trees for translation
Quite often, it is necessary to delete not the entire branch, but only part of it. Again, this cannot be done anywhere. Pruning to translation is a way to remove the extra part of a branch. With the help of a pruner and a hacksaw, we transfer the growth of the branch to strong branches growing in the direction we need, and remove the excess.
In order to properly prune fruit trees like this, as professionals advise, you need to select a strong side branch on a large branch that grows in the desired direction, and remove everything above this branch. The difference from cutting a branch into a ring is that the cut is made so that its plane is a continuation of the remaining branch.
In most cases, they are transferred to a branch directed outward. If the crown is spreading, then it is usually transferred to a branch growing vertically or slightly inside the crown. Drooping branches (characteristic of such varieties of apple trees as Autumn Striped, or Shtreifling, Pepin Saffron) are transferred to horizontal or slightly upward branches.
Removing large branches from fruit trees
If the branch to be removed is large and thick - as thick as a shovel handle or more - then it is wiser and safer to remove it in parts. You will have to make several cuts, but this will protect both people and the tree from injury, and in the end will be less laborious, although it will take a little longer.
The branches only seem light and airy, in fact, their mass can reach several tens of kilograms. As usual, in order to avoid scuffing the bark, we always start sawing from below.
First we need to shorten the branch. We choose an arbitrary place where it is convenient for you to work, and make a cut from below - about half the diameter of the branch. Then we retreat 4-5 cm closer to the trunk and make the second cut - from above. And then the laws of physics begin to work - the branch neatly breaks off along the lines of cuts and the longitudinal line connecting them under its own weight, only in rare cases does it have to be helped with a slight movement of the hand.
If necessary, repeat the combination of two cuts in the next section of the branch. And finally, the last cut. We carry it out as usual - almost always a large branch is cut into a ring, less often - into a translation.
The photo of pruning fruit trees shows how to remove large branches:


How to do spring pruning of fruit trees (with video)
If the winter was frosty and (or) snowless, and there is a possibility that the tree has received damage, do not rush to spring pruning of fruit trees, as they tend to “heal wounds”. A tree, imperceptibly to the human eye, will strive to restore everything that can be restored, and first of all, this concerns educational and conductive tissues. Therefore, after severe winters, buds often bloom later for two weeks or even a month, when the conducting system of the tree begins to work normally again.
After a harsh winter, pruning of fruit trees in the spring is carried out only after full bud break, and only sanitary. The tree needs to use its energy sparingly, it does not need to heal additional wounds, and any other types of pruning can greatly weaken it and reduce vitality, but the excess and dead must be removed. It is likely that some of the branches will begin to bud, but then they will dry out - this is also normal, the tree itself listens to itself and decides that it is more important for it to save. There is nothing wrong with postponing the planned shaping, rejuvenating or restorative pruning for the next season.
In the most difficult cases, when the extent of the damage is large, it will be necessary to confine ourselves to sanitary pruning for several years. However, damaged trees tend to produce a lot of tops, and you can usually start working with them, forming future fruit-bearing branches from them.
Watch the video "Spring pruning of fruit trees" to better understand how this agricultural technique is performed:

Pruning fruit trees for fruiting in the photo
Tops are powerful vertical shoots that grow from dormant buds on old wood, usually in mid-summer. The number of tops per unit length of a branch largely depends on the variety, but it can also be a signal of trouble - the tree shows that it is sick with something, or it is a reaction to incorrect or too strong pruning, in particular, to an incorrect decrease in crown height. A large number of tops is a biological feature of the pear.
Spinning tops grow quickly, with a “wolfish appetite”, and in a season they can reach 1.5 m or more, while also branching.
Since they are directed vertically, their main task is growth, and fruiting from these strong and powerful branches will have to wait several years. In nature, in this way, the tree rejuvenates, new branches grow, and the old ones gradually die off - especially since they literally find themselves in the shadow of tops.
In most cases, tops greatly thicken the crown, and since they also depart at very sharp angles, they must be decisively removed to the ring. In the first couple of weeks of growth, trimming the tops is not necessary, since they are easy to break with your fingers, a small wound will quickly heal. In the future, to trim the tops for fruiting, you will need a pruner and even a hacksaw.
However, there are cases when it is advisable to leave the tops. For example, if the tree is already at an “advanced” age, and you plan to remove the old branch, and there is a strong and well-located spinning top nearby, then a replacement branch can be grown from it. Only for this it is necessary to limit the growth of the top in height. To do this, you need to either trim the tops of fruit trees for translation, or bend them to a position close to the horizontal in order to stimulate the laying of fruit formations. In subsequent years, with a high probability, the "cultivated" top will produce new shoots directed vertically - they will have to be treated the same way.
In case of severe damage, tops are the “source material” for a new crown. If a top is formed next to a large cut, it makes sense to leave it for a year, but be sure to pinch the top - the top draws nutrients and works like a "pump", which accelerates the healing of the wound.
How to properly prune fruit trees and form a crown (with video)
In some cases, especially in the case of trees on a vigorous rootstock, it is necessary to limit the size of the crown. More often it is necessary to limit the height of the crown, less often - the diameter. A common mistake is to prune when forming fruit trees at the same level from the ground, as when cutting a hedge. The result is disappointing and even frightening. Remember the Greek myth of Hercules and the Lernaean Hydra, which had two new heads growing in place of a severed head? Approximately the same happens with incorrectly pruned trees, only the heads usually grow more than two, and even on each cut.
When pruning and shaping fruit trees, gardeners limit the height of the crown for several reasons, the main of which are the difficulties of care, pruning and harvesting, and the tree itself spends too much energy on the “delivery” of nutrients - the young are too far apart, actively functioning, roots and shoots.
Reducing the height of the crown during the formation of fruit trees is carried out strictly for translation. The cut is made over a well-placed branch that you decide to keep. In fact, lowering the height of the crown is the same pruning for translation, only it is not the side branch that is cut, but the top.
If a particular variety is prone to the formation of a large number of tops, then after lowering the height of the crown, the tree will try with a vengeance to take up the lost volume. In this case, a “military trick” will help: pruning is divided into two seasons. In the first year, the crown is lowered - but slightly higher than the planned height. The tree will produce a lot of tops, and here you need to be patient (shortening the tops to limit their growth is not forbidden). In the second year, the crown is lowered at the planned height, and the entire top, overgrown with tops, is removed with one cut. In the future, the tree usually “calms down” and begins to grow in the sizes you specified, and only sometimes you will have to remove single tops.
Here you can watch a video on how to properly prune fruit trees to form a beautiful crown:
Tweezing fruit trees and bending back branches
Special techniques are an alternative or addition to pruning. They are not difficult to perform, but you will need to know in detail what you want to get in the end, and have “three-dimensional thinking”, see the crown in volume - the one that is, and the one that, in the end, will be. And, as in the case of pruning - if in doubt, it is better not to do it.
Pinching, she is pinching - removing the top of a growing young shoot - a yearly growth. It is performed when the shoot is still green, and the top is easily broken off with your fingers - in the place where you decided to limit the growth of the shoot. Usually they pinch over the third or fifth real leaf when the shoot is about 15 cm long. The optimal pinching time is when 2-3 weeks remain before the end of shoot growth, in the middle lane it is about mid-July. A completely similar action is performed when shaping tomatoes, cucumbers and some houseplants - so it is quite possible that you are already familiar with this technique.
It happens that after pinching, axillary buds start to grow. If the shoots growing from them are short - these are future overgrowing branches, do not touch them, and long shoots must be pinched again.
If in some place of the tree there is a strong bud from which a branch will develop, but in this place the branch is not needed, then the bud can be blinded - plucked out with your fingers along with weaker dormant buds located at the base. Do not injure the bark, it is better to blind the sleeping buds later when they start to grow.
Thus, it is possible to level the emerging crown of a young tree or use these techniques when forming artificial crown forms. Due to the size of mature trees, these techniques are of limited use.
Growing tops can be broken out with your hands or with a stick with a hook (even a hook available on the farm will do) - since the growth processes are still ongoing, the wound will quickly heal. It is easiest to break out the tops when they do not exceed 1 5 cm in length, then it is better to use a secateurs, since the likelihood of bark scuffing increases. Spinning tops are easily recognizable by their vertical growth and lighter and often larger foliage. After the tops are removed, sometimes new tops develop from the dormant buds in the same place - they will also have to be removed.
If the tree is still young, then it has few branches and, accordingly, leaves. Hard work with pruners will deprive the tree of foliage, and, consequently, reduce the area of photosynthesis and worsen nutrition. Therefore it makes sense young tree cut unnecessary branches in parts, and at first only limit their growth. In addition, the branches coming from the trunk contribute to the formation of a smoothly expanding trunk, which increases the mechanical strength and stability of the tree.
Bending back branches of fruit trees is in some cases an alternative to removing branches. If in the right side looks only at a branch directed at an ugly angle, you can try to correct the situation. If the angle of departure of the branch from the trunk is very sharp, then it is better not to take risks and cut the branch - with a high probability it will simply break and not bend. The branch is fixed at the desired angle for one or two seasons. If you bend the branches at the end of growth, when lignification begins, then one season is usually enough.
The fastening should be free, with a margin for thickening the branch, therefore, soft material - for example, pieces of rubber - must be placed under the ropes and wires. Keep in mind that during the season the branch increases in diameter by about a centimeter, and a tightly tightened rope bites into the bark and can literally strangle the branch in one season. For the winter, it is better to remove all fasteners, and return them back in the spring.
If the branch is still young and flexible, but still thick, then at the bottom of the limb, you can make several parallel cuts by about a third of the diameter - this will help bend the branch, and the wounds will quickly heal. Thick branches that have lost their elasticity cannot be bent. It should be noted that if the bend turns out to be “humpbacked”, then in the upper part of the “hump” there will be best conditions to feed the kidneys, and it is here that strong and powerful vertically directed tops will grow. In some cases, this is advisable - you grow a strong shoot in that part of the crown where it is necessary, and then remove part of the "mother" branch by pruning for translation - for a young and strong shoot.
Kerbovka and ringing of fruit trees (with video)
Take a closer look at annual growths - in which direction the kidney looks, the escape will be directed there next season. If in this particular place you want to get a strong - or vice versa, weak - branch, then you can use kerbovka.
Kerbovka of fruit trees is carried out in early spring, before the buds begin to swell. We take a garden knife and select a kidney or twig. All that needs to be done is to carefully cut the bark along with a piece of wood in two arcuate movements so that a “crescent” is formed, which we remove from the cut. If a bud or twig needs to be strengthened, then the “crescent” forms a “surprisedly raised eyebrow” from above. Thus, we block the ascending xylem transport flows and do not let them go to the higher-lying kidneys, and the kidney we have chosen receives better nutrition. If a “crescent” is made under the kidney, resembling a smile from ear to ear, then it will weaken the future branch and limit its growth.
You can see how fruit trees are harvested in the video below:
Ringing fruit trees has a similar effect. To do this, a narrow strip of bark is removed. Attention! A strip of bark, contrary to the name of this technique, should not pass along a ring, but along a spiral, or in two half rings with a small gap - thus, traffic flows will be pinched, and not completely blocked. A full ring of bark will disrupt the conduction system, and everything above the ring will dry out pretty quickly - it's easier, faster and more humane to cut a branch with a pruner. The wound must be covered with garden pitch or wrapped with a film to avoid drying out.
Ringing should not be done on the trunk and skeletal branches, so as not to weaken the tree. It is undesirable to perform banding on pear and stone fruit crops, as well as weakened apple trees - there will be more harm than good.
Both in the case of kerbovka and in the case of banding, a narrow strip of removed bark will overgrow rather quickly. The fruit belt is a more country alternative to banding. It can be made from a strip of soft metal with jagged cutouts along the top and bottom edges - this will prevent the metal from cutting into the bark when the branch thickens. The fruit belt is placed on the branch and fixed with wire - it compresses the bark and makes it difficult for the outflow of photosynthesis products. At any time, the fruit belt can be removed, and this is its advantage over banding.
The video of ringing fruit trees shows how this agricultural technique is performed:
Sometimes the growth in thickness occurs so intensely that the bark does not withstand and bursts. To prevent this from happening, furrowing of the bark is used - in the spring, several furrows are applied with a sharp garden knife, running parallel to the branch, 1-2 mm deep - during the season there will be no trace of them.
Pruning fruit trees to improve fruiting
There are several ways to "persuade" a lazy branch to please you with fruits.
First- limit height growth by pruning fruit trees for fruiting, shortening the branch to a bud or branch pointing in the right direction.
Second way- bend the branch (it is absolutely not necessary, and often undesirable, to a horizontal position, but at least the position of the branch must be made vertical). To do this, you can not resort to pruning fruit trees to improve fruiting, but apply stretch marks - they should fix the branch in the desired position, but not injure the bark. You can hang a load on a branch - our ancestors “threatened” barren trees by hanging an ax or various heavy objects in the crown to “disgrace” a lazy tree (and they always added verbal intimidation in the style of “if there is no fruit, I’ll cut it down!”). The branches took a more horizontal position, due to which the balance of plant hormones changed, and fruiting accelerated.
But if the whole tree is “lazy”, then it makes sense to first check how well you take care of it, and also refer to reference books: perhaps you just have one of the old varieties, which are characterized by a late onset of fruiting. So, modern early-growing varieties of apple trees begin to bear fruit at the age of 5-6, and such popular old varieties as Grushovka and Beliy Naliv give their first fruits at the age of 10-12 and even 15 years, being already large trees. In such cases, pruning is needed to form a beautiful and regular crown, but it will not be able to speed up fruiting.
On the other hand, if it is necessary to stimulate the growth of a particular branch of a young tree, it is “pulled up” to the trunk or large branch located above.
This video shows the correct pruning of fruit trees to improve fruiting:
Pruning apple trees is a technique that every gardener needs to own.
By pruning at random, without knowing the rules, gardeners can cause irreparable damage to fruit trees.
Smart pruning - important element in the formation of a well-groomed, consistently fruitful apple orchard.
Before you properly prune an apple tree, it is necessary to carefully study the methods of trimming and their types.
Trimming types
Pruning can be formative, sanitary, rejuvenating and regulating. Formative pruning creates a strong skeleton for the tree, on which only strong, fruit-bearing branches remain. Sanitary pruning is designed to clear the tree of damaged and incorrectly growing branches.
Rejuvenation - removal of old fruit branches. Via regulating pruning the height of the apple tree is restrained, the crown is thinned out, fruiting is regulated.
By intensity, trimming methods are divided into pinching, weak, medium and strong.

- Pinching is used with the active development of annual green growths.
- With weak pruning on young trees, the growth of new shoots is stimulated, skeletal branches are cut off by one quarter.
- With medium pruning, branches are pruned one third. Apply this method on mature apple trees that are more than five years old.
- Strong pruning involves the complete removal of a large number of branches. This is how the crowns of mature trees thin out.
Basic tricks
Trimming on a ring
This technique is used when you want to completely delete a branch. At the point of growth, each branch has an annular outgrowth.
In this place, tissue cells are able to actively divide, so the cut made on the ring heals quickly. It is important to make an even, clean cut. so that about half of the ring remains on the branch, and half on the base.
You can’t cut too far from the base - a stump will remain. The consequence of such pruning is that the stump will dry out, fall out and form a hollow. You can not completely cut the ring from the base, delving into the cambium - this injures the tree.
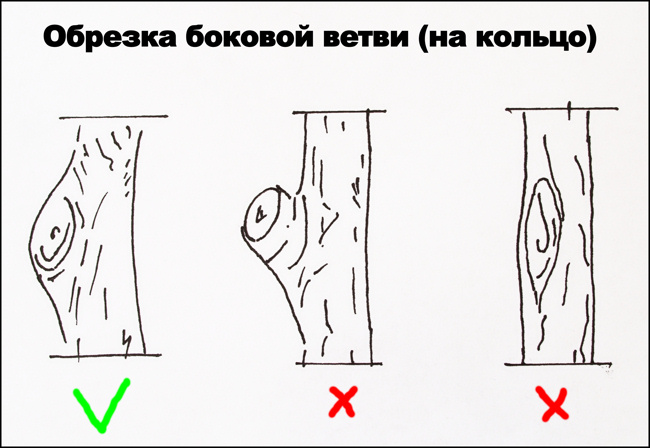
Pruning on the kidney
With partial removal of branches, pruning to the outer bud allows you to expand the crown, reduce the degree of its density.
A cut on a kidney looking inside the crown is used to shoots began to grow inward and the crown became dense.
The correct cutting distance is no more than 50 mm from the selected kidney. Exceed this distance - there will be a stump, underestimate - there is a possibility of damage to the kidney.
Slicing follows immediately cover with garden pitch, oil paint or drying oil, so that the infection does not damage the wound.

An example of a correct kidney pruning.
Large ring sections it is better to pre-disinfect with antifungal drugs, for example, a solution of copper sulfate or iron sulfate (three or five%, respectively).
Terms of work
The timing of pruning is determined by the needs of the trees, not the grower. The best time for work is the very beginning of sap flow. Pruning of trees begins in spring from mid-April and continues until the moment of bud break..
Advice! In early summer, it is convenient to carry out sanitary pruning, as it becomes clearly visible which shoot survived the winter and which one froze.
During this period, it is easy to identify branches infected with infection or pests. In August, pruning can be done in areas where spring return frosts are common. This will slow down the beginning of the tree's vegetation for the next season, and will allow you to save fruit buds.
A good time for pruning apple trees is autumn, when the leaves and fruits have already been shed. The main thing that the next two to three weeks the air temperature did not drop below ten degrees. In the south, in a climate with warm winters the pruning period can continue until February.
Based on the timing of work, methods and types of pruning, you can draw up work schemes in different seasons.
Apple tree pruning scheme for beginners
How to prune apple tree branches in spring?
spring main tasks of the gardener- elimination of the consequences of wintering apple trees, their preparation for the new season. Sanitary pruning is carried out, young apple trees form:

- All broken, burned and frostbitten branches are removed;
- Branches badly damaged by infections or pests are completely destroyed;
- Branches growing inside the crown and forming an acute angle with the trunk are removed;
- Old trees can be rejuvenated;
- Heavy or medium adjustment pruning is carried out, if necessary.
By carrying out regulating pruning in the spring, you can control the amount of the crop. If the previous year the tree gave big harvest, it laid some flower buds. In this case, spring regulatory pruning is not needed.
If the previous year was not rich in harvest, then in spring, the tree must be pruned quite strongly. So the apple tree will have as many fruits as it can grow without spending excessive effort.
How to prune apple trees in summer?
Cardinal pruning is possible only as a reaction to negative natural phenomena.
- Early summer- time to remove diseased branches if the degree of their damage was not visible in the spring;
- End of June- pinch the rapidly growing green shoots so that they do not take food from the main skeleton of the plant, do not shade the crown;
- Anytime those branches that are broken or cracked under the influence of natural factors or the severity of the crop are cut;
- The end of the summer- old branches of adult plants are removed, on which few apples have formed and those that shade young fruit-bearing branches;
- The end of the summer- prune fruit-bearing trees to slow down the start of the growing season next season, if necessary.
If there are no sick and broken branches on the apple trees, in the summer you can limit yourself to only that pruning that regulates the density of the crown. Knowing how to prune an apple tree during the summer months achieve a successful harvest.
How to prune apple trees in autumn?
You can do all those pruning work for which there was not enough time in spring and summer:

- Branches broken by the wind are removed;
- Branches that have broken or cracked under the weight of the fruit are removed;
- After fruiting, sanitary pruning is carried out, designed to get rid of the consequences of harvesting;
- Anti-aging pruning of old apple trees is carried out;
- If during the fruiting period on adult apple trees branches were seen on which the crop was practically absent, they should be removed;
- Branches on which small and deformed fruits have grown are removed;
- Branches that obscure the main fruitful shoots are removed;
- Branches heavily affected by pests, bacterial or fungal infection are removed.
Advice! There is no universal pruning scheme; focus on the individual needs of each apple tree.
The need for pruning depends on many factors. One of them is the age of the orchard.
How to file apple trees of different ages?
Having decided to prune a young apple tree, the gardener sets himself the goal of laying a good foundation for its further development. An old fruit tree is pruned to enhance fruiting, remove crown defects, and save vitality for further growth. Most of the work associated with pruning adult apple trees is aimed at getting rid of diseases and pests.
Although the methods and types of pruning of young and mature trees are the same, the technology of work is different. Consider further how to prune an apple tree by year
annual apple tree
The gardener at this stage has two tasks: to restrain the growth height of the central shoot so that the skeletal side branches develop well, and to form a trunk. Formative pruning of young apple trees should begin one year after planting.
At the age of one year, the seedling consists of a trunk and 2-3 branches. If the central trunk is cut at a height of 0.8 - 1 meter, the growth of lateral shoots will increase. Long skeletal branches must be shortened. Each of them should be shorter by 16-20 cm than the height of the trunk, have three to five buds.
To form the correct trunk, shoots that grow on a seedling at a distance of 40-50 cm from the ground must be removed. Branches that have an angle of up to 60 degrees at the point of growth will not be able to form a good skeleton on their own. They can be dealt with in two ways: remove or try to make them horizontal.
biennial apple tree
If you are thinking about how to prune a 2-year-old apple tree, then you should know that pruning helps to properly lay the tiers of skeletal branches.

The shape of the crown - any, except for the cup-shaped, suggests the presence of two to five large branches on each tier. The interval between the formed levels is approximately 40 - 60 cm and depends on the expected height of the tree.
The branches of each level should be located at approximately equal distance from each other relative to the circumference of the tier. In a two-year-old seedling, skeletal branches are shortened.
If a decision is made to form an apple tree in the form of a bowl, then in the second year of life, the seedling completely remove the central trunk. The cut is made over the first fork of the branches.
In the absence of a center, its role will be taken over by the side branches. An apple tree will be formed, consisting of 2-4 trunks, depending on the number of skeletal branches on the first tier.
Until the age of five, the crown continues to form.
adult apple tree
Starting from the age of five, - the main pruning, which is carried out on fruit trees. Before you start it, make sanitary pruning. When the apple tree is peeled, they begin to rejuvenate:
- Cut off all old branches that are no longer able to produce apples of varietal size and quality;
- Part of the tops is cut out;
- Crossing branches are cut into the ring;
- All branches directed inward and downward are removed;
- The basal and growth near the trunk is destroyed;
The last stage of anti-aging procedures is the shortening of the trunk. Tall trees can be cut to 3.5 - 2.5 meters without damaging the intensity of fruiting. Removing the top allows light to enter the crown, helps to increase the quality of fruits and their quantity.
Important! If the apple tree is more than eight years old, anti-aging pruning should not be done at a time. Losing a large amount of vegetative mass at the same time is a big stress for an old tree.. It is better to distribute the work over several years.
Pruning apple trees on dwarf and columnar rootstocks have their own characteristics.
How to prune a dwarf apple tree?
On a dwarf rootstock, apple trees give abundant harvests, they begin to bear fruit earlier. If dwarf fruit trees are not pruned, their total fruiting period can be reduced to 3 to 5 years.

In the first year of life, the crown skeleton is formed by trimming the trunk. The cut height depends on the variety and is 40-70 cm. The side shoots are cut so that the crown visually looks like ball, cap or triangle.
The closer to the top of the apple tree, the stronger the branches develop. Strong upper branches are shortened, which stimulates the growth and development of shoots in the center of the crown. Tree branches on dwarf rootstocks, if they are healthy, rarely cut completely. Most often, two to four kidneys are left on them.
As soon as the apple tree begins to bear fruit, the number of flower buds should be regulated so as not to overload the apple tree with fruits. Under the weight of fruits dwarf varieties can threaten not only the fracture of the branches. A tree can uproot itself from the ground.
How to prune a columnar apple tree
The shape of the crown of columnar apple trees is special. The width of such a tree does not exceed 50 cm, it has no long lateral branches. Regular pruning columns are not required. But sometimes the apple tree needs pruning.
Damage to the top of the trunk
Top damage - one of the most common problems columnar apple tree. Damage is usually caused by frost and pests, then by the beginning of the season the apical part of the trunk dries up and dies. These processes force gardeners to trim the top.
The peculiarity of pruning shoots at the crown is that it is necessary not only to cut off the central shoot, but also to find a replacement for it. If this is not done, the apple tree forms several trunks on top, will lose the shape of the column. To create a new top, choose the strongest shoot that grows vertically.
The remaining vertical branches are cut off, leaving two to three buds from the base. The former crown is removed at the point of contact with the chosen leader.
To avoid the need for pruning, the top of the columns should be wrapped for the winter.
How to cut an apple tree while maintaining the shape of the crown?
The first year of growth, columnar varieties, as a rule, do not require the gardener to intervene in the process of crown formation. Starting from the age of two, young growths begin to compete with fruit-bearing branches, take food from them.

It is during this period that the gardener must intervene and adjust the ratio of growth of the main branches and increments:
- All the shoots that the apple tree has formed are pinched at the same distance from the trunk, which is 25-30 cm;
- In the third and following years, pinching is carried out at a distance of 30-40 cm;
- Starting from the fourth year, three-year branches are partially removed.
The features of pruning side shoots are that with systematic pinching, the columnar apple tree will not need pruning. Since pinching is a more gentle procedure, the apple tree is not injured, does not experience stress.
Attention! Full wrapping of columnar apple trees with covering material in several layers for the winter is recommended. So, during the period of severe frosts and sharp temperature fluctuations, they will not suffer flower buds, trunk and, most importantly, the bark of an apple tree.
The need for special supportive care is experienced by any apple tree after the pruning procedure.
How to prune an apple tree: video of the correct technique
If you do not know how to properly prune an apple tree, we recommend watching this video:
And in this video, see the details and subtleties of spring pruning of apple trees:
Apple tree care after pruning
After pruning, fruit trees need watering and top dressing. If pruning was carried out in the spring, it is necessary to add fertilizers to the soil of the trunk circle, which contain nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in equal parts.

After autumn pruning, fertilizers are applied, which contain potassium and phosphorus - they stimulate wound healing, strengthen the bark of the apple tree. Nitrogen fertilizers in the autumn should be avoided.
The introduction of nitrogen in the fall will give impetus to the development of new shoots, as a result, the wood of annual growths will not have time to fully mature, the apple tree will not prepare for wintering. As a result, cuts made in the fall may be susceptible to frostbite.
When fertilizing, fertilizer application rates should be strictly observed. Overfertilizing apple trees will do more harm than good.

Apple pruning plan.

How to prune an apple tree by year.

How to prune an apple tree in autumn.

How to prune apple trees to form a tree crown.
Instead of a conclusion
When preparing to prune an apple tree, it must be remembered that by cutting each branch, one should answer the question “why?”. There is an answer - cut. The answer is no, so this branch can remain on the apple tree.
If a bacterial or fungal infection rages in the area - garden pruning should be postponed. Each slice is a potential entry point for microbes.
Proper pruning is the key to the health and fertility of the orchard.
In contact with
