The most reliable of the existing foundations is considered monolithic slab with a grillage. The correct design name is the bowl plate. However, individual developers often confuse foundation elements. In this case, the grillage is the basement part (stiffeners).
The combined foundation in the form of a tape on a monolithic slab is used in several cases:
- unstable soil - for some reason, the developer is not satisfied with the pile-screw foundation, it was decided to fill the slab on loose, loose, undermined, bulk soils;
- the need for a high base - a brick, block base has a smaller resource than reinforced concrete, the designer decided to pour the base on the slab into the formwork;
- basement floor in the project - if at a depth of 1.7 m it is not possible to reach layers with a normal bearing capacity, the tape serving as the walls of the basement level rests on the slab.
Developers usually call the first two options a slab with a grillage, in which the slab has a small (0.2 - 0.4 m) deepening, or is poured above the ground. However, the construction of a buried slab with a high monolithic belt is the most difficult to manufacture. Therefore, this technology will be considered below.
If, according to the results of calculations, the slab on the surface meets the operational requirements, the grillage is necessary as the basement of the building, it is enough to reduce the height of the formwork. There are no other differences in these technologies.
Research and calculation
Geological survey results are required to calculate the characteristics of the slab. They are produced by specialized organizations that have SRO approval, in accordance with the standards of SP 11-105, 11-104, 11-102,.
- the distance between the two reinforcement belts is 10 cm;
- thickness of reinforcement of periodic section - 10 - 14 mm;
- protective layer (the depth to which the reinforcement is immersed in concrete) - 2 - 7 cm (usually 3 cm below, 4 cm above).
The bearing capacity always has a multiple reserve, even for a three-story cottage with an attic (the maximum value allowed for low-rise buildings).
Strip foundation under load-bearing walls on the upper edge of the slab in this case must meet the conditions:
- normal support of wall material - overhang is allowed brickwork 10 cm (in several rows) in each direction, for log cabins, "frame frames", 20 cm of tape width is enough;
- strength against lateral loads - there is no backfilling inside the basement floor, lateral movements of the soil during swelling are not compensated by anything.
If these conditions are met, the minimum reinforcement dimensions are automatically maintained, similar to those above for the slab part of the foundation.
Layout and excavation

We dig a foundation pit for the future foundation.
For concreting the slab at a depth of 1.7 - 2.5 m, a pit of the appropriate size is required. However, when marking a building spot, the following factors must be taken into account:
- when installing the formwork for the slab part, workers need access to the outer perimeter of the structure (+ 0.5 - 0.8 m to the size of the pit);
- to install the formwork panels of the tape part, you will need cords along the axes of the bearing walls + strings along the outer edges of the tape.
For the manufacture of a drainage system along the perimeter of the foundation sole, it is not necessary to additionally increase the pit. The slab and foundation tape must be waterproofed with gluing, coating, volumetric (penetrating) compounds before backfilling.

We make depressions for drainage, if necessary.
Unlike a floating slab on the ground surface, the engineering systems input nodes are located in the basement walls, which dramatically increases the maintainability of communications. The markup takes place according to the standard technology:
- castoffs 1.5 - 2 m from the edge of the pit - two pieces for each axis, two cords on each wall ( side faces tapes);
- line around the perimeter of the pit - lime mortar or with chalk on the ground, they draw contours for excavation, special accuracy is not required here.

We cover geotextiles at the bottom of the pit.
In view of the large volume of work and the need to remove soil from the site, it is extremely difficult to do without special equipment in this case.
Substrate

We fall asleep to the bottom of 20 cm of crushed stone. Be sure to tamp it with a vibrating plate.
Any foundation requires a non-metallic underlayment. The base of the trench is leveled with sand, gravel, drainage properties of the structure are provided. There are several substrate options:
- sand 40 cm - every 10 cm is leveled, compacted with a vibrating plate (at the end of the process, there should be no traces of workers' shoes on the sand), it is used at a depth of groundwater level (groundwater level) 1 m below the slab;
- crushed stone 40 cm - tamping is similar to the previous case, it is used at high groundwater level, since the inert material has better drainage properties, stability of geometry (sand in water turns into a viscous substance, the calculated soil resistance decreases, the foundation subsidence is possible);
- sand 20 cm + crushed stone 20 cm - the most popular option for individual developers (sand is cheaper than crushed stone), the technique is suitable for high groundwater levels, however, to protect the hydroglass insulation from damage, a 5 cm footing will have to be poured over the crushed stone;
- crushed stone 20 cm + sand 20 cm - the technology allows you to do without a foundation that protects the waterproofing carpet from crushed stone punctures.

We fill in 20 cm of sand on top of the crushed stone, we also compact it with a vibrating plate.
The bottom layer of inert material is laid on a geotextile carpet to prevent rubble or sand from mixing with the ground. The strip foundation rests on the slab, is connected to it by common reinforcement, the underlying layer is not required.
Before making the substrate, it is necessary to mount the drainage system according to the scheme:
- inspection wells - located in the corners of the foundation, every 4 m on the sides, made of plugged pipes (smooth, corrugated) with a diameter of 40 - 100 cm;
- horizontal sections - corrugated, smooth-walled perforated drains in a double-layer geotextile winding, interrupted inside the wells to provide access for a tool to clean the system.
For drainage, trenches are made around the perimeter of the foundation at the depth of the base of the slab. They must have a slope towards the common side, connected in one circuit, with an underground tank, into which the drains will be collected. To ensure a high drainage resource, the wells are mounted on a 10 cm layer of crushed stone 5/20 mm over the geotextile layer. The pipes are filled up on the sides, on top with the same natural filter, and again covered with geotextiles.
The industry produces prefabricated wells for drainage systems with ready input nodes horizontal pipes... They cost more homemade options, provide reliable tightness of joints.
Concrete preparation and waterproofing
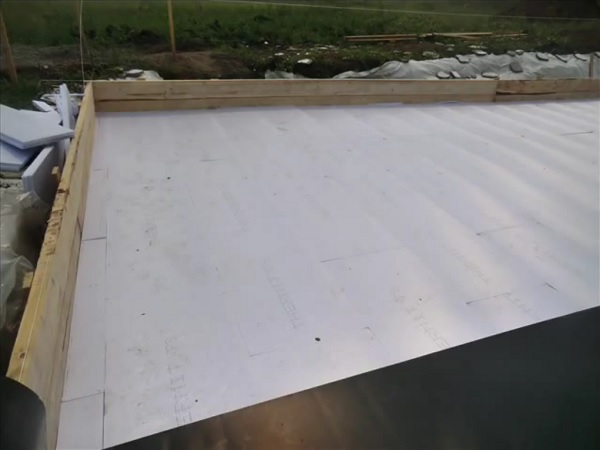

We expose the formwork for the slab and lay the insulation, if provided by the project.
The base of the slab foundation needs protection against wetting, pressurized groundwater. For this, membranes, polyethylene films (0.15 mm minimum), roll materials (hydrostekloizol, Bikrost, Technonikol) are used.

We install waterproofing.
If the upper sub-base is made of rubble, the integrity of the waterproofing carpet will be compromised by pebbles (multiple punctures after loading the foundation). Therefore, in this case, a footing is used to protect the waterproofing:
- a formwork with a height of 7 - 10 cm is mounted along the perimeter of the pit;
- 5 - 7 cm of B7.5 concrete screed is poured without reinforcement.
The foundation tape has no contact of the sole with the ground, therefore it is waterproofed later, after the entire structure has been stripped.
Formwork and reinforcement

We assemble the reinforcement cage for the slab with vertical outlets for the tape part.
Due to the fact that the strip foundation is concreted between two formwork panels, interior which has nothing to support in the absence of a slab, the structure is poured in two stages. First, the slab is concreted, after a strength gain of 70%, the formwork for the tape is mounted.
Therefore, when reinforcing the slab part, it is necessary to release vertical rods from it to bond with the tape. Shields along the outer perimeter are installed slightly above the design mark. This will prevent the concrete from spilling out during vibration compaction and will facilitate smoothing the surface. Reinforcement is made according to the following scheme:
- lower belt - a mesh with a cell 10 x 10 - 20 x 20 cm made of bars with a periodic section of 10 - 16 mm, build-up along the length with an overlap of 40 - 50 cm, a gap of joints in adjacent rows of 60 cm minimum, installation on polymer or concrete pads 2 - 4 cm to provide a protective layer;
- upper chord - exactly the same mesh, installed on clamps made of round reinforcement 6 - 8 mm to provide a gap between chords, an upper protective layer;
- lintels along the perimeter - U-shaped elements of 6 - 8 mm reinforcement, connecting the rods of both belts together.
To liaise with top tape rods bent at right angles are tied to the upper mesh. They should protrude from the slab by 40 - 60 cm, be located in accordance with the tape reinforcement scheme.
Slab part
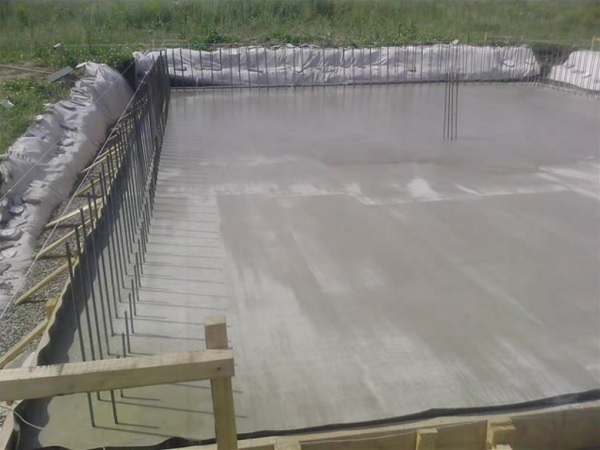

We fill the stove and wait for at least 7 days (at a temperature not lower than +25 C °).
The slab is concreted according to the standard scheme. The perimeter is filled with a mixture from the far corner with periodic vibration compaction, smoothing the surface. Dumping of concrete from a height of more than 2 m is prohibited, the maximum quality even without using a deep vibrator is achieved when using a concrete pump.
In addition, it is impossible to supply a mixture of unsatisfactory quality through the concrete pump. This, by default, guarantees the developer the maximum resource of the structure, despite the rental of expensive special equipment. The approximate timing of demoulding at + 5 - + 10 degrees 15 - 29 days, respectively. In hot weather (+ 20 - +30 degrees), the hydration process is reduced, you can remove the shields for 4 - 7 days, respectively.
Base part for floating slab

We finish the reinforcement of the tape part.
The installation of the formwork for the tape on a slab cast without deepening into the ground looks like:
- external shields - installed on the ground, pressed against the side edge of the slab, fixed with jibs to the ground;
- internal shields - rest on the slab, jibs are attached to the concrete surface;
- after laying the reinforcement cage, the formwork panels are additionally tightened with wire.
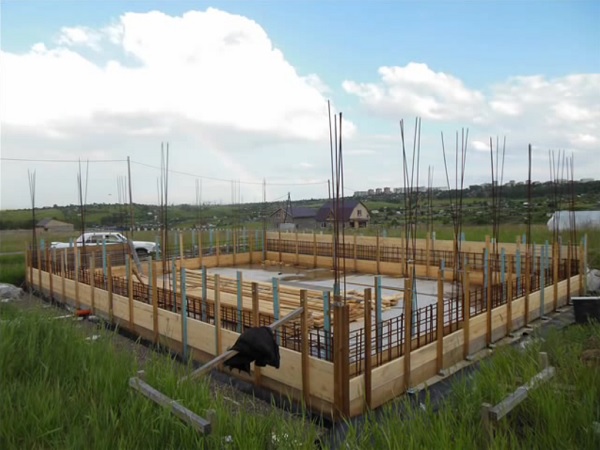

We expose and fix the formwork for the strip part of the foundation.
It is necessary to install embedded (pipes) for ventilation ducts in the formwork panels. The reinforcement is stacked in two rows with protective layers, the longitudinal rods are tied to rectangular clamps to ensure stable spatial geometry. Pouring is done in one direction at a time. The entire thickness of concrete must be compacted with a deep vibrator nozzle.

We pour concrete into the formwork.
Strip foundation on a recessed slab
In projects with an underground floor, the height of the strip part of the slab foundation reaches 2 - 2.5 meters. This complicates concreting in one step due to the large volumes of the mixture. Therefore, stage-by-stage pouring technology is often used. It is forbidden to mount vertical jumpers in the corners, cut the reinforcement for the installation of shields. Therefore, shields with cuts are used, into which the rods are passed, the remaining slots are filled with polyurethane foam.
With phased concreting, the next section can be poured after 50% of the strength of the previous one. The joint is cleaned with a metal brush, steam, grinder. All film from the surface of hardened concrete must be removed completely.
Due to the large volumes of concreting, formwork requires a lot of lumber and plywood. When processing inner surface shields plastic wrap after stripping, these materials can be used in the future (partitions, subfloors, roofing, rafter system).
Two reinforcement belts at such a belt height are no longer enough, more belts are added every 50-70 cm in the middle part. At the same time, the size of the clamps increases. additional elements to ensure stable geometry (side gaskets for cover).
Pouring and maintaining concrete
When filling the tape formwork with the mixture, it is necessary to follow the standard concreting technology:
- a layer of 60 cm around the perimeter - usually the length of the nozzle of a deep vibrator is of this size, the compaction is done in layers until the design level is reached;
- the size of the coarse filler - depending on the reinforcement step, crushed stone is 5/10 mm or 5/20 mm.
With a high GWL, to reduce the cost of waterproofing concrete structures, it is advisable to add a penetrating composition to mixers, concrete mixer. By default, concrete will receive water-repellent properties, will be able to withstand pressurized waters.
Caring for concrete in winter consists in heating by covering methods (polystyrene, straw), placing a heating cable inside the structure. In the summer, it is enough to cover the formwork with a film in the rain, pour the first three days from a watering can to prevent cracking. The most effective wet compress is a layer of sand, sawdust, constantly moistened with a hose.
After stripping the slab, the foundation tape is waterproofed with a continuous layer of bituminous mastics, roll material or impregnations. All concrete surfaces should be covered with these materials.
The above slab-grillage foundation is the most reliable of all existing ones. It is suitable for buildings with a basement level, but is very expensive.
Advice! If you need contractors, there is a very convenient service for their selection. Just submit in the form below detailed description works that need to be completed and you will receive offers with prices from construction crews and firms. You can see reviews of each of them and photos with examples of work. It is FREE and non-binding.
Price per square meter with material - from 3500 rubles.
The foundation is established during the construction of structures of any size. Ideal for water-saturated and weakly bearing soils(if the device of a high base is not required, and the plate itself is a floor).
- Reinforcement along the entire bearing plane, reinforcement A3 Ø 12-16mm (GOST 5781-82).
- Sand pillow - 30cm.
- Stove - 25cm.
- Concrete M-300 B22.5 P4 F200 W6
- The term for making the foundation is 5-7 days.
Monolithic slab foundation - this is a solid monolithic reinforced concrete slab, laid under the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe future house. home distinctive feature this type of foundation from all others is the largest supporting area, which allows for high stability rates of the future structure. That is why it is chosen for heavy houses, as well as for construction on soils with low bearing capacity.
This foundation, thanks to large area, is better able to withstand the forces of heaving of the soil, under their action, the entire plate falls and rises, and not its individual pieces and elements. As a result, a house or other object built on such a foundation is reliably insured against distortions.
Some technical features of a slab monolithic foundation.
A monolithic foundation slab is laid on a previously prepared base - a compacted cushion of sand and gravel. The thickness of the sand cushion is 20 cm or more. After the base cushion is prepared, it is necessary to proceed with the waterproofing.
The next stage is the fabrication of the foundation reinforcement cage, which should consist of two meshes (upper and lower). It is important to take into account that the meshes of the frame must be interconnected. For the manufacture of a reinforcing cage of a monolithic foundation, you can use reinforcement with a cross section (in other words, ribbed) with a diameter of 12-16 mm.
It is important to understand that the requirements for reinforcement for a monolithic foundation are significantly different and an order of magnitude higher than for a strip foundation. If the tape is subjected to a bending load only along, then for a monolithic similar loads appear both in the longitudinal and transverse directions. It is easy to explain this: the width of the strip foundation is less than its height.
Moreover, in a monolithic foundation, torsional loads can also occur. Therefore, the reinforcing frame in this type of foundation must be completely made of ribbed reinforcement, which provides better adhesion to concrete, as a result, higher strength indicators.
The reinforcement rods must be installed at a distance of 20-40 cm from each other. If we take the average and lay the reinforcement in the foundation with a step of 30 cm, then it is easy to calculate that it will take 1 square meter: 3 times 1 meter of reinforcement along, the same amount across for each stiffness belt (and they, as we remember, two), here it is also worth adding 2 meters of reinforcement to connect the stiffening belts to each other - as a result, 14 meters of reinforcement.
As you can see, the consumption of reinforcement for the manufacture of a monolithic foundation is significantly higher. Than for other types of foundation arrangement. The same can be said about the consumption of concrete, which allows us to conclude that the cost of building a foundation-slab is an order of magnitude higher than any other type of foundation.
A monolithic foundation can be smooth or with stiffeners, which are most often made on the underside of the slab. This makes it possible to make the slab as a whole more resistant to various kinds of loads and deformations, and also creates a significant obstacle to its horizontal displacement. The top side of the monolithic foundation slab remains smooth and may well serve as a basement floor or basement floor future home. In the case of building a house without a basement or basement, the use of a monolithic slab foundation is considered inappropriate, irrational.
Depending on the type of soil on the construction site and its characteristics monolithic foundation can be shallow or deeply buried. To arrange a buried monolithic foundation, it is necessary to dig a pit, which by itself implies the performance of a much larger amount of work. The advantage of this solution is the fact that as a result, such a foundation is able to provide maximum bearing capacity and is able to withstand even the heaviest buildings.
In individual construction, the use of a buried monolithic slab foundation is a rarity, since there is no need for such high indicators of bearing capacity, there is no need to extract a large amount of soil (to dig a pit). If it is necessary to increase the strength indicators of a monolithic foundation, then a shallowly buried monolithic foundation-slab is chosen.
For its arrangement, it is enough just to remove the fertile soil layer and cover a pillow of sand and gravel. As a result, the upper surface of the foundation slab is slightly, but still above ground level. To provide such a foundation with resistance to heaving of the earth as a result of its freezing in winter period, the soil around the foundation is insulated.
As you can see, the construction of a monolithic slab foundation is costly. building materials, but in the end it allows you to provide a large support area and high strength indicators.
In order to understand whether there is a need for such a large supporting area for construction, it is necessary at the design stage of the house to calculate the load of the house on the foundation and correlate these indicators with the bearing capacity of the soil in this area where construction is underway or planned.
It is advisable to choose a slab monolithic foundation in case high level groundwater, on soft soils. If the characteristics of the soil make it possible to do with a smaller support area, it is worth giving preference to the strip type of foundation, which will significantly reduce the cost of laying the foundation for building a house.
The construction of any house, regardless of climate conditions, design features of the building itself and the materials from which it is planned to be erected, begins from the base - the foundation. There are several varieties of them, each of which is suitable for certain conditions and has both pros and cons. The choice of the base should depend on the characteristics of the soil, the proposed layout of the house, the number of storeys of the building, the materials from which the structure will be built, plays a significant role and financial question: in some cases, the foundation can cost a relatively small amount, and sometimes its cost reaches a quarter of the total cost of the entire construction. The foundation slab for a house is quite well known, and it is used both for the construction of light buildings and for the construction of massive and large cottages of two or more floors. More often it is laid under large and expensive buildings, since its cost is usually very high.
Such a base looks like a slab cast from a monolith or created from component parts under the whole house with a deepening, usually slightly higher than the degree of soil freezing. It is easier to make a monolithic base, since it is not necessary to order a concrete pump for this, but you can get by with a concrete mixer and not order other heavy equipment. When creating a precast slab, you will need at least a truck with a crane, since the foundation blocks, from which the base plate is usually assembled, cannot be moved otherwise. 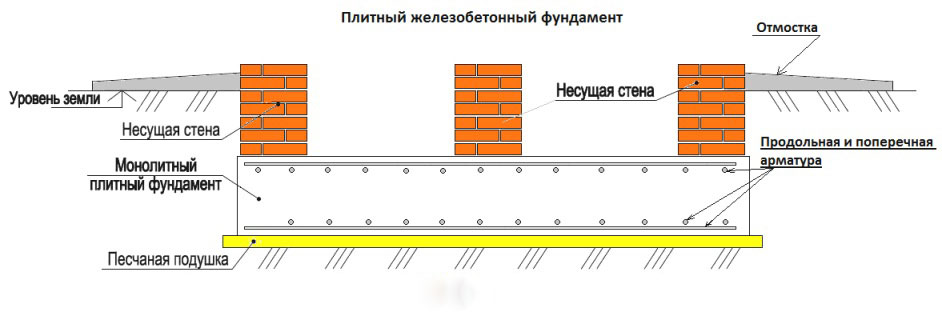
Important! When creating a slab base, it should be remembered that there will be no basement or basement in the house: such a structure does not allow this.
For which house is a slab foundation suitable?
Such a foundation can be laid under a building with any structure, architectural concept and weight: the slab has a high bearing capacity, it is resistant to impact environment, besides, it can be made in any shape, especially if we talk about a monolith. A house on a slab foundation can be made of expanded clay concrete blocks, gas blocks, foam blocks, bricks, it can have one or more floors: when pouring or laying a slab of appropriate thickness, it will withstand such a load. In addition, an important plus is the fact that the slab can be arranged on a weak, mobile and mixed soil: a single structure guarantees the stability of the structure and a uniform shrinkage process.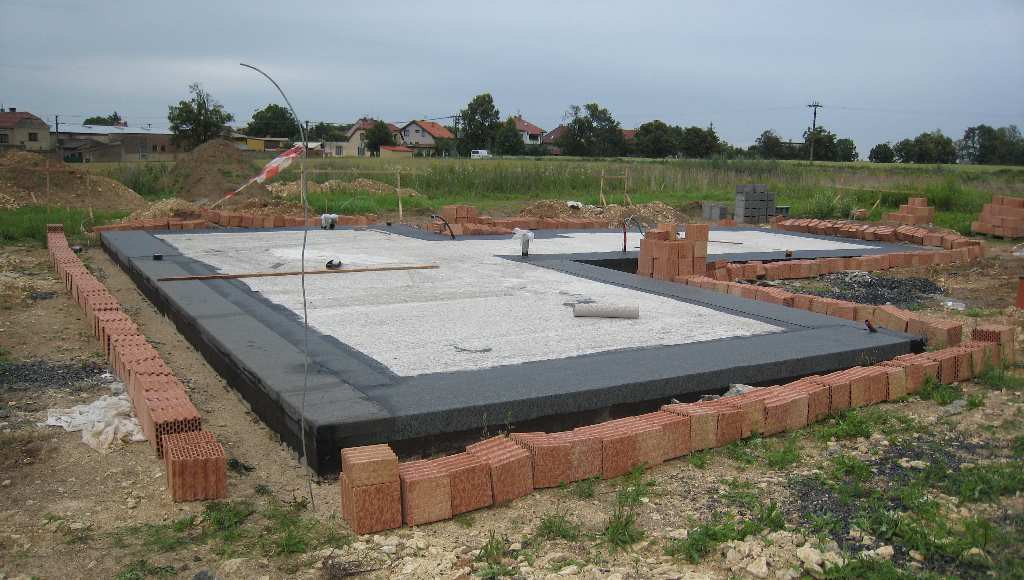 
The algorithm for creating a slab will depend on what type was chosen for the construction of the house. If we are talking about a monolith, then first of all, a pit is dug under it, a groundwater drainage system is arranged if necessary, then a cushion of sand and gravel is made, after which the formwork is made. A reinforced frame is immersed in it to give strength, after which concrete is poured into the formwork (usually they take the M300, M400, M500 brand). When the process is complete, the plate should dry: in the summer it takes about a month. If you plan to build a house on a foundation slab from prefabricated blocks, then you do not need to make formwork and the body from reinforcement: the blocks are installed next to each other, fastened with a mixture based on cement. Such a foundation is ready for further construction after 2-3 weeks. 
conclusions
The most reliable, durable, but also expensive foundation for a house is a slab, which can be solid or prefabricated. It can be installed on almost any type of soil for the construction of even a complex and heavy house, and the only drawback of such a foundation is perhaps a considerable cost.
Slab foundation under the house video:
For individual residential buildings construction organizations offer four types of foundations, different in design and principle of the device. A solid monolithic slab seems to be costly, but a reliable and stable base. She is able to stand without deformations and other problems for more than one decade. Consider what makes up the cost of pouring a foundation slab. And advice from construction experts will prompt possible ways optimization of costs.
A shallow base is chosen when erecting country houses on weak and problematic soils: swampy terrain, soil with difficult terrain, seismic zone, abundance groundwater with the risk of flooding. Usually these are buildings made of bricks, aerated blocks or wood. The slab foundation has good resistance to uneven loads and high spatial rigidity. The large support area allows many times to reduce the pressure on the ground, evenly distributing the mass of the building along the entire perimeter.
Laying a solid slab base requires reinforced preparatory work using a large number of materials. This negatively affects the amount of final costs.
Construction contractors offer standard rates for foundation concreting, the change of which depends on several factors:
- overall dimensions of a monolithic slab;
- the volume of geodetic and earthworks;
- construction of the foundation - from digging a pit to dismantling the formwork;
- the amount of building materials;
- attraction of special equipment;
- remoteness from the city limits.

As a result, the construction of the foundation for a turnkey house costs the customer from 200 thousand to 1.5 million rubles.
| Foundation size, m | Monolith area, m 2 | Cost of work, rub / m 2 with plate thickness |
|||
| 250 mm | 300 mm | 350 mm | 400 mm | ||
| 6x6 | 36 | 5800-7220 | 6130-7670 | 6900-8080 | 7050-8350 |
| 7x9 | 63 | 4300-5700 | 5000-6170 | 5220-6480 | 5700-6920 |
| 8x8 | 64 | 4000-5580 | 4300-5900 | 5000-6230 | 5400-6670 |
| 9x9 | 81 | 4100-5680 | 4500-6050 | 5200-6400 | 5620-6900 |
| 10x10 | 100 | 3900-5120 | 4200-5570 | 4800-5950 | 5300-6370 |
| 10x12 | 120 | 3800-4960 | 4100-5330 | 4520-5770 | 5200-6340 |
| 12x12 | 144 | 3700-4810 | 3960-5190 | 4400-5600 | 4800-6050 |
| 13x13 | 169 | 3550-4640 | 3800-5090 | 4300-5470 | 4600-5870 |
| 14x14 | 196 | 3200-4570 | 3700-5050 | 4200-5430 | 4600-5860 |
| 15x15 | 225 | 3100-4540 | 3700-5000 | 4100-5540 | 4750-5970 |
| 16x16 | 256 | 3100-4540 | 3700-5000 | 4100-5400 | 4700-5900 |
What is the final construction price of?
In design and estimate documentation, up to 50% of expenses are labor costs. For each specific case, the design of the foundation slab is developed by an experienced designer and calculated in individually... The likelihood of additional strengthening of the base under the load-bearing walls is also taken into account. For one-storey buildings, a slab 200-300 mm thick is quite enough. A house of two or more levels requires raising the level of the foundation pouring to 400-1000 mm.
List of stages of construction of a slab foundation
1. Geodetic work: analysis of the terrain, marking the site, binding the base.
2. Excavation of soil by a mechanized method.
3. Manual reworking of the pit bottom, leveling marks.
4. Reinforcement of the deepening with geotextile fabric, which does not allow mixing of bulk building materials with the ground.
5. Construction of sand and gravel cushion, consisting of several layers:
- sand base 200-300 mm thick, poured with water and rammed with a vibrating plate;
- installation of a geotextile separating membrane;
- filling crushed stone with a fraction of 20-40 in a layer of 100-200 mm with subsequent compaction;
- flooring technical film under the concrete.
6. Installation of plank and timber formwork.

7. Two-layer base reinforcement with corrugated steel bar d 12-16 mm - frame strapping with 200x200 mm cells.

8. Installation of a sleeve for laying engineering systems in the house.
9. Pouring prefabricated liquid concrete of the M-400 or M-500 brand using deep vibrators.
10. Dismantling of the formwork after complete hardening of the monolithic slab.
11. Cleaning of the territory.
According to statistics, every second company invests in total costs the full amount of costs: the price for work, the cost of building materials, fasteners, their delivery, unloading. In addition, the depreciation of the tool (hand, gasoline, electric) and the cost of special equipment are taken into account. If a concrete works fall in the winter period, the estimate is additionally increased due to the operation of the heating transformer.
How to reduce the cost of slab foundation?
Turning to a contractor, the customer receives a turnkey package of construction services, backed by quality guarantees. Despite the outstanding advantages of a monolithic slab, many people are upset by the high price of a bookmark. In some cases, it reaches half the cost of a building box.
The prices for building the foundation of a residential building can be significantly reduced by abandoning the services of contractors and taking on partial or full execution of the work. In this case, you will not have to pay for the labor of hired teams and the rental of tools.

The following measures will help to reduce the cost of the work process by 1.5-2 times:
- alignment land plot and planning the foundation with your own hands;
- independent purchase and delivery of fittings, fasteners, formwork boards;
- ordering factory concrete of a lowered grade M200 or M300;
- preparation of a mortar mixture in a household mixer directly on the site;
- manual concreting;
- replacing gravel with sand when installing a cushion under a monolith.
We recommend: pouring the foundation for building a house from the company midero.byBefore concluding a contract for laying a foundation slab, contact several companies and compare the volumes of services provided and the cost of work. There are contractors who undertake transportation costs, do not require paying for the rental of tools, or offer the installation of communications along with pipes (water supply, sewerage) as a gift.
